Induction furnace
Induction heating is a heating method. The heating by the induction method occurs when an electrically conductive material is placed in a varying magnetic field. Induction heating is a rapid form of heating in which a current is induced directly into the part being heated. Induction heating is a non-contact form of heating.
The heating system in an induction furnace includes:
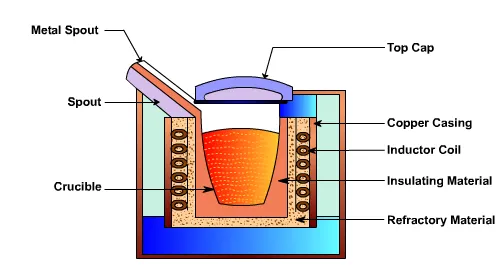
The induction heating power supply sends alternating current through the induction coil, which generates a magnetic field. Induction furnaces work on the principle of a transformer. An alternative electromagnetic field induces eddy currents in the metal which converts the electric energy to heat without any physical contact between the induction coil and the work piece. A schematic diagram of induction furnace is shown in Figure 16. The furnace contains a crucible surrounded by a water cooled copper coil. The coil is called primary coil to which a high frequency current is supplied. By induction secondary currents, called eddy currents are produced in the crucible. High temperature can be obtained by this method. Induction furnaces are of two types: cored furnace and coreless furnace. Cored furnaces are used almost exclusively as holding furnaces. In cored furnace the electromagnetic field heats the metal between two coils. Coreless furnaces heat the metal via an external primary coil.

Figure 16: Schematic of a Induction Furnace
Advantages of Induction Furnace
Disadvantages of Induction Furnace