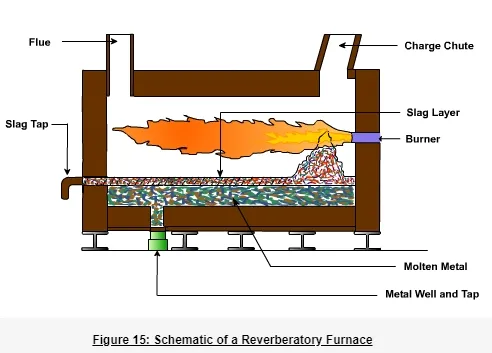
Reverberatory furnace
A furnace or kiln in which the material under treatment is heated indirectly by means of a flame deflected downward from the roof. Reverberatory furnaces are used in opper, tin, and nickel production, in the production of certain concretes and cements, and in aluminum. Reverberatory furnaces heat the metal to melting temperatures with direct fired wall-mounted burners. The primary mode of heat transfer is through radiation from the refractory brick walls to the metal, but convective heat transfer also provides additional heating from the burner to the metal. The advantages provided by reverberatory melters is the high volume processing rate, and low operating and maintenance costs. The disadvantages of the reverberatory melters are the high metal oxidation rates, low efficiencies, and large floor space requirements. A schematic of Reverberatory furnace is shown in Figure 15
