Natural Resources in India & World
Natural resources are highly valued because human beings are dependent on them to fulfil their fundamental needs that changes with time. While natural resources are distributed in all through the world, specific resources often require particular conditions and so not all natural resources are spread equally. Consequently, nations trade their natural resources to make certain that their needs can be fulfilled.
In simple term, natural resources are material and constituent formed within environment or any matter or energy that are resulting from environment, used by living things that humans use for food, fuel, clothing, and shelter. These comprise of water, soil, minerals, vegetation, animals, air, and sunlight. People require resources to survive and succeed. Everything which happens naturally on earth are natural resources that is minerals, land, water, soil, wind that can be used in many ways by human being. It can be explained by several environmentalist scholars that a natural resources is any kind of substance in its natural form which is needed by humans.
The general classifications of natural resources are minerals for example as gold and tin and energy resources such as coal and oil. The air, forests and oceans can also be categorised as natural resources. Theoretical studies have documented that Land and water are the natural resources, which include Biological resources, such as flower, trees, birds, wild animals, fish etc., Mineral resources, such as metals, oil, coal, building stones and sand, and other resources, like air, sunshine and climate (UNEP, 1987). Natural Resources are used to make food fuel and raw materials for the production of finished goods (Adriaanse, 1993). Natural resources change in value over time, depending on what a society most needs or considers most valuable.
Resource distribution is defined as the geographic occurrence or spatial arrangement of resources on earth. In other words, where resources are located. Any one place may be rich in the resources for people desire and poor in other. The availability of natural resources is based on two functions that include the physical characteristics of the resources themselves and human economic and technological conditions. The physical processes that govern the formation, distribution, and occurrence of natural resources are determined by physical laws over which people have no direct control. We take what nature gives us. To be considered a resource, however, a given substance must be understood to be a resource. This is cultural, not purely a physical circumstance.
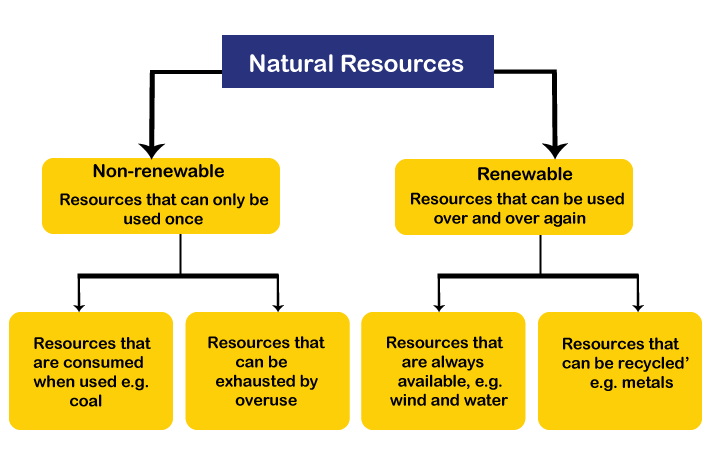
The various types of natural resources are often categorizes as renewable and non-renewable resources.
Renewable can be described by scientists as a resource that can be replenished or reformed either naturally or by systemic recycling of used resources. Renewable is resource or source of energy that is replaced naturally or controlled carefully and can therefore be used without the risk of finishing it all (Oxford dictionary). Another way to define is a resource that is able to be renewed and be capable of being begun or done again. Renewable resources are usually living resources such as plants and animals and they also include air and water. These resources are termed as ‘renewable’ because they can usually reproduce or restock themselves. Renewable resources are significant aspect of sustainability. Renewable resources are valuable because they provide green energy. Renewable natural resources include those resources beneficial to human economies that demonstrate growth, maintenance, and recovery from exploitation over an economic planning horizon. The natural environment, with soil, water, forests, plants and animals are all renewable resource. In the case of air and water, they are renewable elements because they exist as part of a cycle which allows them to be reused. Renewable resources can only exist as long as they are not being used at a greater rate than they can replenish themselves (David Waugh, 2002).
Non-renewable resources cannot be re-produced or re-grown and are, therefore, they are available in limited supply. Scholars affirmed that Non-renewable resource is a natural resource that does not renew itself at a sufficient rate for sustainable economic extraction in meaningful human timeframes. Non-renewable resources are resources for which there is a limited supply. The supply comes from the Earth itself and, as it typically takes millions of years to develop, is finite. Non-renewable resources can generally be separated into two main categories; it includes Fossil fuels, nuclear fuels. Coal is considered a non-renewable resource because even though it is continually being formed, it is incapable to refill its stock at a rate which is sustainable (David Waugh, 2002). A non-renewable resource cannot maintain the demands for current human needs while still preserving the ecosystem for future generations.
Types of natural resources:

Distribution of resources is varied. Since the formation of earth, it has experienced numerous physical processes which have resulted in great variations between different areas. Since natural resources often need specific conditions in which to form, they are not distributed evenly across the world. For instance, Coal is usually found in areas which were originally swampland during the greatest coal-forming era in history, the Carboniferous Period. It has been observed that as the distribution of natural resources is varied, it is not unusual for some nations to have one type of natural resource in plentiful quantity and for other countries to have many different types but with only a small supply. This indicates that the nations which are rich in some kind of natural resources do not necessarily use them all themselves. As an alternative, countries often export the natural resources that they have plenty of and import those which they require.
It has been observed that generally populace tend to settle and cluster in places that have the resources they need to survive and prosper. The geographic factors that most influence where humans settle are water, soil, vegetation, climate, and landscape. Because South America, Africa, and Australia have fewer of these geographic benefits, there is less population as compared to North America, Europe, and Asia.
Due to uneven resource distribution, human beings migrate to other regions where plenty of resources are available. Majority of people often migrate to a place that has the resources they need or want and migrate away from a place that lacks the resources they need. Lively examples in historical migrations are The Trail of Tears, Westward Movement, and the Gold Rush related to the desire for land and mineral resources. Economic activities in a region relate to the resources in that region. Economic activities that are directly associated with resources include farming, fishing, ranching, timber processing, oil and gas production, mining, and tourism. Many business scholars have affirmed that nations may not have the resources that are important to them, but business movement enables them to acquire those resources from places that have. For example, Japan has very limited natural resources but it is one of the wealthiest in Asia. Sony, Nintendo, Canon, Toyota, Honda, Sharp, Sanyo, Nissan are prosperous Japanese corporations that make products that are highly-desired in other countries. As a result of trade, Japan has enough wealth to buy the resources it needs.
It has been seen that most of the countries in the world are having natural resources. Some have less amount while other countries are rich in particular natural resource. Economists stated that natural resources add wealth to nations.
When it is evaluated for resource distribution around the world, Australia has many natural resources. These resources include mineral resources, such as copper, gold and diamonds, energy resources, such as coal, oil, and uranium, and land resources that are used for farming and logging. These resources are financially important to Australia. Many people consider that the monetary system of Australia is resource dependent, which means that if these resources were to be depleted, Australia’s economy would suffer. Australia has more coal than is needed and so exports it to countries like Japan which are lacking in it. Australia does not, however, produce enough oil to meet the demands of consumption and it is forced to import it. Some countries, especially developing nations, have the availability of natural resources but they do not use them fully. Sometimes countries do not have a great demand for the resource or simply lack the technology to develop or extract it. Rich transnational corporations (TNCs) often pay a fee to do the mining or extraction of the natural resources and then export them to developed countries.
Mineral resources: Australia is major producer of minerals at global scale. The most important mineral resources in Australia are bauxite, gold and iron ore. Other mineral deposits in Australia include copper, lead, zinc, diamonds and mineral sands. A majority of Australia’s minerals are excavated in Western Australia and Queensland. The minerals mined in Australia are exported, or shipped abroad.
Energy resources: Australia has huge deposits of coal. Coal is generally found in the eastern part of the country in the Sydney and Bowen basins. Majority of Australian coal is exported to nations like Japan, Korea, Taiwan and Western Europe. The rest of the coal mines in Australia are burned for electricity within Australia.
Natural gas is also plentiful in Australia. Natural gas is used to heat homes and power certain types of vehicles. Natural gas reserves in Australia are mostly found in Western Australia and central Australia. Since most of these reserves are far away from metropolitan centres, gas pipelines have been built to transport natural gas to cities such as Sydney and Melbourne. Some of this natural gas is exported from where it is collected. Natural gas collected in Western Australia is exported directly to Japan in liquid form.
Australia is also rich in uranium and supply at global level. Uranium is used to produce nuclear power. Nuclear power and uranium mining are both highly contentious, as people are concerned for their environmental impact, because uranium can produce toxic energy.
Lastly, Australia has many land resources. Australian soil is used to grow food in the form of crops and to produce food for raising livestock, such as cattle. Australian forests are used as a source of wood for building and making paper.
When discussing about natural resources in Africa, It is revealed in reports that Africa is rich in natural resources including diamonds, salt, gold, iron, cobalt, uranium, copper, bauxite, silver, petroleum and cocoa beans, but also woods and tropical fruits. Russia is excessively capable of natural resources, but industrial development was hindered until the twentieth century by their Siberian inaccessibility. Russia now produces 20 per cent of the world’s natural gas, and oil is also a valuable commodity. Russia is self-sufficient in all major industrial raw materials, and contains reserves of less essential, but significant natural resources, including diamonds and gold.
Industrialized nations have benefit over poor countries because if they do not have the quantity or type of natural resources which they require, they can afford to import them. Developed countries need to import natural resources because they depend on them for the development of their economy. Their use of natural resources is considered as a well-planned and constructive industry. It has been recommended that developed nations use more of the natural resources of world as compared to other developing nations. Reports have signified that while developed countries account for 25 percent of the world’s population, they use 75 percent of the world’s natural resources.
Geographical Distribution of Oil and Natural Gas Deposits: It was documented in reports that about 70 % of global conventional oil and natural gas reserves are concentrated inside a so called Strategic Ellipseî stretching from Middle East to the North of West Siberia. Main consuming regions in 2004 were North America, Austral-Asia, and Europe, for natural gas North America, CIS and Europe.
Development of primary energy consumption worldwide and projections of IEA until 2030
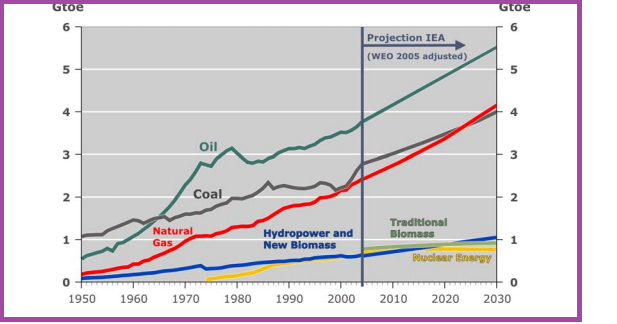
When appraising the distribution of natural gas, it is found in reports that about 41 % of global reserves are in the Middle East, about 32 % in the CIS countries and about 8 % in Africa.
Regarding iron core resource in the world, USA is rich in this resource. Ore is mined in the red mountains and Birmingham Valley. Northern New Jersey, the states of Utah, Nevada and California also are rich in iron core. In Canada, there are three main areas where iron core is mined that include Ontario, Quebec and new found land. In Europe, Germany, France, Sweden and UK are large producer of Iron ore. Ukraine has the sixth position in the world in producing iron ore and it produced 4.32 per cent of the world production in 2006. Krivoi Rog of Ukraine possesses best iron ore having 68.5 per cent metallic percentage. It contributes 75 per cent production of Ukraine. The estimated reserves of the region are more than 200 million tons. Other regions of Ukraine are Zaporozhe, Zdanow, Lipetsk and Kerch Peninsula.
South Africa is also major iron ore producing country of the African continent and ranks 8th in the world iron ore production. In South Africa Transvaal is the main iron ore-producing centre. Transvaal is having high-grade ore with 60 to 65 per cent iron content. The total reserves have been estimated at 10 billion tons in South Africa. The average annual production of South Africa is 4 million metric tons.
Distribution of key natural resources in South Asia:
When appraising the regions of South Asia, it has been found that these provinces have enormous natural resource and ecological and biological diversity. Many researchers have recognized that The Southeast Asian states today are rich in natural resources and are major world producers of rubber, tin, copra, palm oil, petroleum and timber (Chia 1999). However population growth and economic development are intimidating the region’s rich heritage through the expansion and intensification of agriculture, the unrestrained growth of industrialization, the destruction of natural homes and urban extension. Southeast Asia has lavish source of hydrocarbon resources natural gas and petroleum.
Natural resources
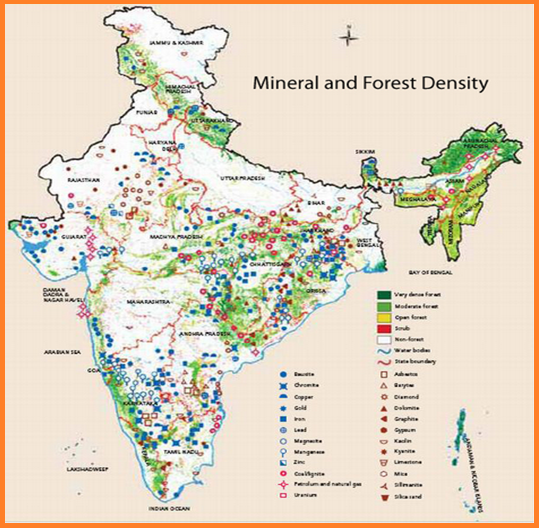
Traditional government accounting systems do not consider the significance of these natural resources. The South Asia’s nation governments have recognised several areas for growth that include nature-based tourism, mining, ecosystem, biodiversity and agriculture which will concurrently help diversity the economic and decrease poverty. In order to fulfil all development goals, the governments need to optimize use of natural resources. The main concentration of South Asia is to understand the value of natural resources that leads to better decisions for development. Valuing the environment and incorporating natural resources into national accounts, it can support better to nation’s economy.