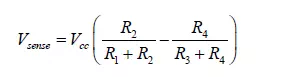Bridge Measurements
The sensitivity of a sensor can be increased by incorporating it in a bridge arrangement. Impedance varying sensors are often arranged in DC or AC Wheatstone bridges. In some types
of measurement (e.g. in strain measurements) it is possible to perform a differential measurement comparing the outputs of 2 sensors subjected to opposite stimuli (for example, tensile and compression).
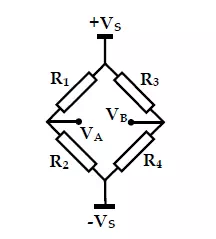
Figure 1.11: Wheatstone bridge
The Wheatstone Bridge Circuit
Current to the bridge flows through the excitation leads. The differential output voltage is measured via the sense leads, generally using an instrumentation amplifier. Frequently more
than one transducer is used in the bridge to increase the sensitivity of the measurement. To cancel temperature effects, a ‘dummy’ transducer is often used on the same side of the bridge as
the measuring sensor; this dummy sensor is not subject to the same input signal as the measuring sensor. The response equations of the Wheatstone bridge are well known: