Optical pyrometer( Disappearing filament Type)
Monochromatic brightness radiation thermometer
Basic Principle of optical pyrometer:
The principle of temperature measurement by brightness comparison is used in optical pyrometer. A colour variation with the growth in temperature is taken as an index of temperature.
This optical pyrometer compares the brightness of image produced by temperature source with that of reference temperature lamp. The current in the lamp is adjusted until the brightness of the lamp is equal to the brightness of the image produced by the temperature source. Since the intensity of light of any wavelength depends on the temperature of the radiating object, the current passing through the lamp becomes a measure of the temperature of the temperature source when calibrated.
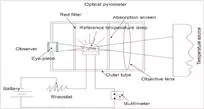
Construction of optical pyrometer:
The main parts of an optical pyrometer are as follows:
An eye piece at one end and an objective lens at the other end.
A power source (battery), rheostat and millivoltmeter (to measure current) connected to a reference temperature bulb.
An absorption screen is placed in between the objective lens and reference temperature lamp. The absorption screen is used to increase the range of the temperature which can be measured by the instrument.
The red filter between the eyepiece and the lamp allows only a narrow band of wavelength of around 0.65mui
Operation of optical pyrometer:
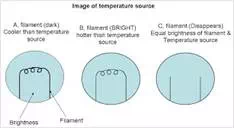
When a temperature source is to be measured , the radiation from the source are focused onto the filament of the reference temperature lamp using the objective lens. Now the eyepiece is adjusted so that the filament of the reference temperature lamp is in sharp focus and the filament is seen super imposed on the image of the temperature source. Now the observer starts controlling the lamp current and the filament will appear dark as in figure (a) if the filament is cooler than the temperature source, the filament will appear bright as in figure (b) if the filament is hotter than the temperature source, the filament will not be seen as in figure (c) if the filament and temperature source are in the same temperature.
Hence the observer should control the lamp current until the filament and the temperature source have the same brightness which will be noticed when the filament disappears as in figure (c) in the superimposed image of the temperature source [ that is the brightness of the lamp and the temperature source are same]. At the instance, the current flowing through the lamp which is indicated by the millivoltmeter connected to the lamp becomes a measure of the temperature of the temperature source when calibrated.
Applications of optical pyrometer:
Optical pyrometers are used to measure temperature of molten metals or heated materials.
Optical pyrometers are used to measure temperature of furnace and hot bodies.
Advantages of optical pyrometer:
Physical contact of the instrument is not required to measure temperature of the temperature source.
Accuracy is high + or – 5’C.
Provided a proper sized image of the temperature source is obtained in the instrument, the distance between the instrument and the temperature source does not matter.
The instrument is easy to operate.
Limitations of the Optical pyrometer:
Temperature of more than 700’C can only be measured since illumination of the temperature source is a must for measurement.
Since it is manually operated, it cannot be used for the continuous monitoring and controlling purpose.