How to Calibrate a Thermometer using Primary Calibration Method
The temperature measuring devices such as mercury-in-glass thermometer, bimetallic thermometer, resistance thermometer and thermocouples can be calibrated using a primary calibration method.
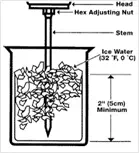
In this method, the introduced accurately known samples of the variable are the ice point and steam point. Using this ice point and steam point, the instrument is checked, set and thus calibrated. As the instruments (thermometers) are calibrated with reference to the equilibrium temperature of substances, it is primary calibration.
To set the ice point, the sensing element (bulb) and the stem of the instrument (thermometer) is surrounded with a mixture of crushed ice and water which is open to atmosphere. Now the instrument will show some indication on its scale and this is taken as ice point (zero point) on the scale of the instrument.
Now to set the steam point (as shown in the diagram), the instrumentís sensing element (bulb) and the stem is surrounded by steam to its full depth. Care should be taken to see that the instrument does not contact the boiling water. Now the instrument will show some indication on its scale and this is taken as the steam point (100íC) on the scale of the instrument.
Thus by giving known temperature inputs (ice point and steam point), the instrumentís (thermometerís) response is noted and calibrated.