Biodiversity
DIVERSITY IS KEY
Healthy ecosystems, interdependent webs of living organisms and their physical environment, are vital to all life on Earth. Our ecosystems provide us with clean air, fresh water, food, resources and medicine.
Biodiversity, the variation of life on Earth, is a major factor in nature's resilience. In a biodiverse ecosystem, if the environment changes and some organisms can no longer thrive, others can take their place and fulfill essential functions. It is often the most overlooked species that are the most important to healthy ecosystems. Insects, for example, play an essential role in pollinating flowering plants — a third of the food we eat depends on animal pollinators.

THE SIXTH MASS EXTINCTION
Since life appeared on Earth, there have been several mass extinctions in which many species were wiped out because of catastrophic climate change, volcanic activity, the impact of an asteroid or other reasons we have not yet discovered.
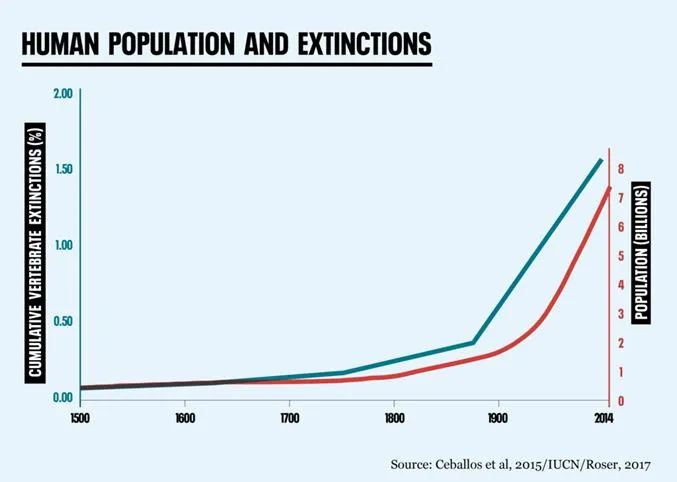
The plants and animals which currently live on Earth have continued to evolve over the 65 million years since the last mass extinction. But many scientists consider the huge reduction in biodiversity since the emergence of humans is now on the scale of another mass extinction. This is known as the Anthropocene extinction or sixth mass extinction.
WWF's latest Living Planet Report estimates that we have lost 60% of all vertebrate wildlife populations since 1970. That's more than half of all birds, mammals, reptiles, amphibians and fish gone in just 50 years. During that time, our population has more than doubled, increasing from 3.7 billion to over 7.8 billion today. Invertebrates, while understudied, aren't faring any better. A German study found that flying insect populations (including pollinators) have crashed by three-quarters since 1989, reflecting similar trends around the world.
In its landmark 2019 report, IPBES reported that one million species are now at risk of disappearing for good and according to the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, 41% of amphibians, 25% of mammals, 34% of conifers, 13% of birds, 31% of sharks and rays, 33% of reef-building corals, and 27% of crustaceans are threatened with extinction.
Some countries are worse off than others. The 2016 State of Nature report concluded that the United Kingdom was one of the most nature-depleted countries in the world.
Biodiversity loss is attributable to several causes but by far the biggest culprits are habitat destruction and overexploitation of species, driven by our exploding numbers and unsustainable consumption.
HABITAT DESTRUCTION
Ever more people need ever more space. Damaging human activity continues to encroach on natural environments, thereby destroying the habitats of countless species. As our numbers rise, cities and industrial areas are growing and merging into each other, fragmenting the remaining habitat and leaving isolated “islands” of natural populations of plants and animals too small to survive. According to IPBES, only one quarter of land areas and one third of oceans remain relatively undamaged by human activity.

OVEREXPLOITATION
Ever more people need ever more things. Humankind’s relentless consumption of resources such as timber, oil and minerals is continuing to destroy natural habitats around the globe. We are also putting enormous pressure on populations of wild species, both by bushmeat hunting in the developing world and by large-scale industrial fishing in our seas. Wildlife poaching and trafficking still present a huge threat to many species, including rhinos, tigers and pangolins.

AGRICULTURAL INTENSIFICATION
Ever more people need ever more food. In order to meet the unsustainable consumption patterns of the developed world and feed the numbers of people living on the Earth today, humanity has developed agricultural systems which rely on monocultures, artificial fertilisers and pesticides. Monocultures are increasingly susceptible to disease whilst widespread pesticide use destroys insect populations indiscriminately. In addition, the growing pressure on food supplies means an increasing proportion of agricultural land is farmed intensively, with fewer off seasons or fallow years in which to recover. Currently, livestock farming contributes to more climate emissions than the entire transport sector and is the biggest cause of deforestation. Runoff from farms pollutes water bodies and causes harmful algal blooms and the collapse of fish stocks.

CLIMATE CHANGE
Ever more people produce ever more climate emissions. Our planet is on the verge of a climate crisis due to our endless production of greenhouse gases including carbon dioxide and methane. We are headed for a 3-4 °C warmer world by the end of the century if nations' current climate ambitions are delivered on. We are already seeing species decline due to global temperature increase. Every half a degree of warming has a huge knock-on effect on ecosystems, with mobile species running out of areas to migrate to and temperature-sensitive organisms like corals undergoing massive die-offs. When keystone species like reef-building corals disappear, the rich and complex ecosystems they support collapse as well.

POLLUTION
Ever more people produce ever more waste and pollution. As populations increase, the disposal of waste from households, agriculture and industry, becomes an increasingly serious issue. Our oceans are becoming choked with plastic waste which is killing millions of animals, from sea turtles to whales. The Ellen MacArthur Foundation estimates that by 2050, there will be more plastic than fish in the sea. As well as affecting the lives of humans, noise, light and chemical pollution all damage the health of wild species.

INVASIVE SPECIES
Ever more people means ever more travel. Human travel across the world has a very large emissions footprint but it has also allowed the spread of invasive species, both accidental and intentional. As a consequence of the introduction of non-native species to some areas, such as rabbits and cats in Australia, goats on St. Helena, and American mink in Great Britain, we have put many vulnerable ecosystems at risk, threatening native species and diminishing biodiversity.