Markov Analysis
transition probability matrix is developed to determine the
probabilities of job incumbents remaining in their jobs for the forecasting
period.
The technique is named after Russian mathematician Andrei Andreyevich Markov,

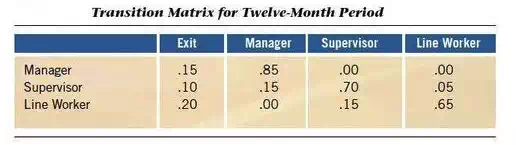
A transition matrix, or Markov matrix, can be used to model the internal flow of human resources. These matrices simply show as probabilities the average rate of historical movement from one job to another. Figure 2-12 presents a very simple transition matrix. For a line worker, for example, there is a 20% probability of being gone in 12 months, a 0% probability of promotion to manager, a 15% probability of promotion to supervisor, and a 65% probability of being a line worker this time next year. Such transition matrices form the bases for computer simulations of the internal flow of people through a large organization over time.