SmartMedia
The SM (SmartMedia) card is a type of flash memory card. It was one of the first memory cards to be produced and used in digital cameras, and other electronic devices. The SmartMedia card had a smaller capacity, ranging from 2 MB to 128 MB, and physical dimensions of 45mm x 37mm x .76mm. The picture shows an example of an 8 MB SmartMedia card.
NAND flash memory
NAND flash memory is a specific type of flash memory that uses memory cell connections organized in series, resembling a NAND logic gate. This setup is in contrast to NOR flash memory, which connects memory cells in parallel. The result is a memory chip that uses the physical area of the chip more efficiently, allowing for greater memory capacity on a similarly-sized form factor.
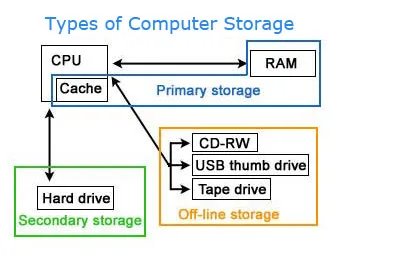
Memory
Computer memory is any physical device capable of storing information temporarily, like RAM (random access memory), or permanently, like ROM (read-only memory). Memory devices utilize integrated circuits and are used by operating systems, software, and hardware.
Below is an example of a 512 MB DIMM computer memory module. This memory module connects to the memory slot on a computer motherboard.
Memory can be either volatile and non-volatile memory. Volatile memory is memory that loses its contents when the computer or hardware device loses power. Computer RAM is an example of volatile memory. It is why if your computer freezes or reboots when working on a program, you lose anything that hasn't been saved. Non-volatile memory, sometimes abbreviated as NVRAM, is memory that keeps its contents even if the power is lost. EPROM is an example of non-volatile memory.
As mentioned above, because RAM is volatile memory, when the computer loses power, anything stored in RAM is lost. For example, while working on a document, it is stored in RAM. If it were saved to non-volatile memory (e.g., the hard drive), it would be lost if the computer lost power.

It is very common for new computer users to be confused by what parts in the computer are memory. Although both the hard drive and RAM are memory, it's more appropriate to refer to RAM as "memory" or "primary memory" and a hard drive as "storage" or "secondary storage."
When someone asks how much memory is in your computer, it is often between 1 GB and 16 GB of RAM and several hundred gigabytes, or even a terabyte, of hard disk drive storage. In other words, you always have more hard drive space than RAM.
When a program, such as your Internet browser, is open, it is loaded from your hard drive and placed into RAM. This process allows that program to communicate with the processor at higher speeds. Anything you save to your computer, such as a picture or video, is sent to your hard drive for storage.
Each device in a computer operates at different speeds and computer memory gives your computer a place to quickly access data. If the CPU had to wait for a secondary storage device, like a hard disk drive, a computer would be much slower.
There are several types of memory for computers. They are listed below.
ROM is separated into three categories:
· PROM
· EPROM
· EEPROM
There are six types of RAM:
· EDO RAM
· SDRAM
· DDR RAM
· DDR2 RAM
· DDR3 RAM
· DDR4 RAM
These types of memory all fall into the general categories of SIMM or DIMM.