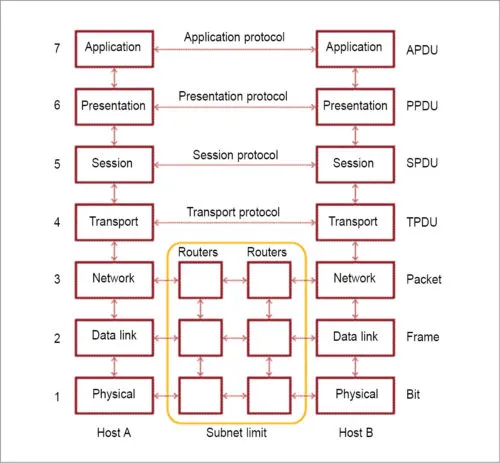
 Fig. 1: Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model
Fig. 1: Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference modelWith newer technologies like 5G and IoT, standardisation becomes necessary for the devices to communicate with each other. Let us explore the latest wireless standards in detail along with their applications.
The cool quotient of communication devices is increasing immensely as we advance towards newer wireless means for connectivity. The need to update benchmarks for these systems also arises alongside. The latest wireless communication technology standards have to adhere to the requirements and ensure better security and quality than the previously adopted standards.
According to Bipin Pradeep Kumar, co-founder and director, Gaia Smart Cities, “Standardisation is a complex subject that needs to be looked at different levels. At the communication level, apart from Wi-Fi, unlicenced long-range technologies like Sigfox and LoRaWAN are being adopted widely. Then there are several short-range technologies as well, like Zigbee and z-wave. All these technologies should be able to coexist. On the protocol side, there are so many options. Prominent among them is MQTT (Message Queue Telemetry Transport), which is an ISO20922 standard.”
Direct device-to-device (D2D) communications technology is being considered to provide low-power, high-data-rate and low-latency services to 5G network users.
Rajan Mathews, director general, Cellular Operators Associations of India (COAI), says, “The latest iteration of mobile broadband technology, 5G, will bring in new unique network and service capabilities.” “It will be a thousand times faster than 4G and will provide Internet access in areas that have not yet been tapped because of various roadblocks,” he adds.
5G is hopping to a new level where innumerable devices can be connected to each other using D2D standard and where security breach is extremely difficult. This D2D technology would be beneficial even when the network is out of range. A wide array of sensor networks can be used for home security systems, energy grids and entertainment.
Basically, 5G is 4G technology integrated with worldwide wireless web. Currently, in terms of bandwidth, it offers more than 1Gbps as against 4G’s 200Mbps.
“We are very excited about the possibilities this opens up in terms of network architecture, particularly in view of 5G’s aim to connect new industries and empower unique service scenarios,” said Woojune Kim, vice president and head of next-generation strategy, Samsung Electronics, in a press release.
D2D standard was introduced by Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP)—one of the most powerful standardisation bodies in the world. 3GPP brings together seven different telecom development associations, namely, Association of Radio Industries and Businesses (ARIB), Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions (ATIS), China Communications Standards Association (CCSA), European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), Telecommunications Standards Development Society, India (TSDSI), Telecommunications Technology Association of Korea (TTA) and Telecommunication Technology Committee, Japan (TTC).
The largest executed and adopted standard for wireless communication, IEEE 802 mainly works on Layers 1 and 2 of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model. Almost the complete set of standards within IEEE 802 consists of the present and future packet networks.
 Fig. 1: Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model
Fig. 1: Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model
IEEE 802 LAN/MAN Standards Committee consists of about a thousand participants. IEEE 802 standard addresses different ranges, from personal-area networks to local-area networks, metropolitan area networks and regional-area networks. These, however, are not restricted by size so far.
IEEE 802 standard finds numerous 5G and other applications:
1. IEEE 802 projects and decides architecture, internetworking, security, network management, time-sensitive networking and protocol layers above Layer 2.
2. IEEE develops standards for Ethernet environments like data centres, wide-area networks and automobiles.
3. IEEE 802.11ad and P802.15.7 support extremely high level of throughput under 5G. IEEE 802.11ah is best suited for spectrum under 1GHz, with focus on the Internet of Things (IoT) support.
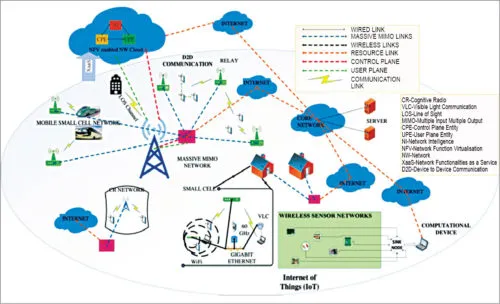 Fig. 2: The Internet of Things
Fig. 2: The Internet of Things
4. The IEEE 802.21 working group is creating the P802.21.1 standard to provide media-independent services such as home energy management system, software-defined radio access networks, radio resource management and device-to-device communication.
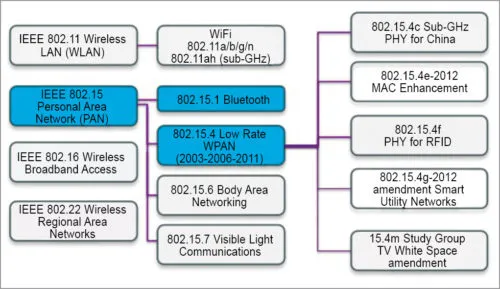 Fig. 3: IEEE Standards
Fig. 3: IEEE Standards