Motherboard
The main circuit board which connects all the device on a microcomputer; Also called main board or system board
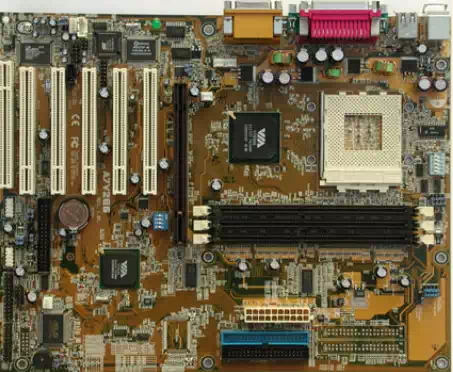
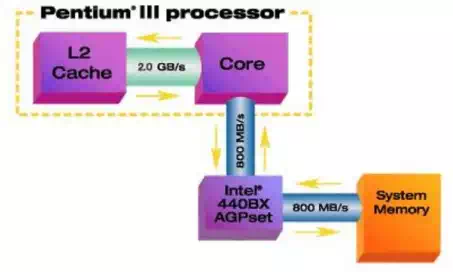
· Chipset
– The chipset controls the system and its capabilities. It is the hub of all data transfer.
– Chipsets are integrated, and are not upgradable without buying a whole new motherboard.
– Some of the items it dictates
∗ Memory controller
∗ Real-time clock
∗ Keyboard and mouse controller
∗ Secondary cache controller
∗ PCI bridge
∗ EIDE controller
· Motherboards are designed for specific Processors. A single motherboard cannot be used with different types of Processors.
· The different system bus speeds supported by the Motherboard should be of prime consideration.
· Form Factors
– The form factor is the physical size and dimensions of the motherboard. The form factor determines the general layout, size, and feature placement on a motherboard.
∗ Baby AT
∗ ATX
∗ Proprietary

· Onboard devices - Video/Audio/LAN
– Lower cost.
– Lesser Flexibility.
· Upgradability
– Bus speeds supported.
– Number of expansion slots.
– Number and Types of IO ports available.