Input / Output Devices
These devices are used to enter information and instructions into a computer for storage or processing and to deliver the processed data to a user. Input/Output devices are required for users to communicate with the computer. In simple terms, input devices bring information INTO the computer and output devices bring information OUT of a computer system. These input/output devices are also known as peripherals since they surround the CPU and memory of a computer system.
a) Input Devices
An input device is any device that provides input to a computer. There are many input devices, but the two most common ones are a keyboard and mouse. Every key you press on the keyboard and every movement or click you make with the mouse sends a specific input signal to the computer.
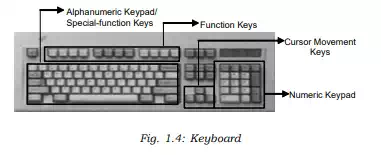
· Keyboard: The keyboard is very much like a standard typewriter keyboard with a few additional keys. The basic QWERTY layout of characters is maintained to make it easy to use the system. The additional keys are included to perform certain special functions. These are known as function keys that vary in number from keyboard to keyboard.
· Mouse: A device that controls the movement of the cursor or pointer on a display screen. A mouse is a small object you can roll along a hard and flat surface (Fig. 1.5). Its name is derived from its shape, which looks a bit like a mouse. As you move the mouse, the pointer on the display screen moves in the same direction.

· Trackball: A trackball is an input device used to enter motion data into computers or other electronic devices. It serves the same purpose as a mouse, but is designed with a moveable ball on the top, which can be rolled in any direction.
· Touchpad: A touch pad is a device for pointing (controlling input positioning) on a computer display screen. It is an alternative to the mouse. Originally incorporated in laptop computers, touch pads are also being made for use with desktop computers. A touch pad works by sensing the user’s finger movement and downward pressure.
· Touch Screen: It allows the user to operate/make selections by simply touching the display screen. A display screen that is sensitive to the touch of a finger or stylus. Widely used on ATM machines, retail point-of-sale terminals, car navigation systems, medical monitors and industrial control panels.
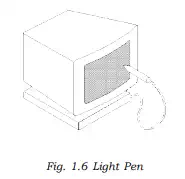
· Light Pen: Light pen is an input device that utilizes a light-sensitive detector to select objects on a display screen. (Fig. 1.6)
· Magnetic ink character recognition (MICR): MICR can identify character printed with a special ink that contains particles of magnetic material. This device particularly finds applications in banking industry.
· Optical mark recognition (OMR): Optical mark recognition, also called mark sense reader is a technology where an OMR device senses the presence or absence of a mark, such as pencil mark. OMR is widely used in tests such as aptitude test.
· Bar code reader: Bar-code readers are photoelectric scanners that read the bar codes or vertical zebra strips marks, printed on product containers. These devices are generally used in super markets, bookshops etc.
· Scanner: Scanner is an input device that can read text or illustration printed on paper and translates the information into a form that the computer can use. A scanner works by digitizing an image. (Fig. 1.7)

b) Output Devices:
Output device receives information from the CPU and presents it to the user in the desired from. The processed data, stored in the memory of the computer is sent to the output unit, which then converts it into a form that can be understood by the user. The output is usually produced in one of the two ways – on the display device, or on paper (hard copy).
· Monitor: is often used synonymously with “computer screen” or “display.” Monitor is an output device that resembles the television screen (fig. 1.8). It may use a Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) to display information. The monitor is associated with a keyboard for manual input of characters and displays the information as it is keyed in. It also displays the program or application output. Like the television, monitors are also available in different sizes.

· Printer: Printers are used to produce paper (commonly known as hardcopy) output. Based on the technology used, they can be classified as Impact or Non-impact printers.
Impact printers use the typewriting printing mechanism wherein a hammer strikes the paper through a ribbon in order to produce output. Dot-matrix and Character printers fall under this category.
Non-impact printers do not touch the paper while printing. They use chemical, heat or electrical signals to etch the symbols on paper. Inkjet, Deskjet, Laser, Thermal printers fall under this category of printers.
· Plotter: Plotters are used to print graphical output on paper. It interprets computer commands and makes line drawings on paper using multicoloured automated pens. It is capable of producing graphs, drawings, charts, maps etc. (Fig. 1.9)

· Facsimile (FAX): Facsimile machine, a device that can send or receive pictures and text over a telephone line. Fax machines work by digitizing an image.
· Sound cards and Speaker(s): An expansion board that enables a computer to manipulate and output sounds. Sound cards are necessary for nearly all CD-ROMs and have become commonplace on modern personal computers. Sound cards enable the computer to output sound through speakers connected to the board, to record sound input from a microphone connected to the computer, and manipulate sound stored on a disk.