The BIOS and the Boot Process
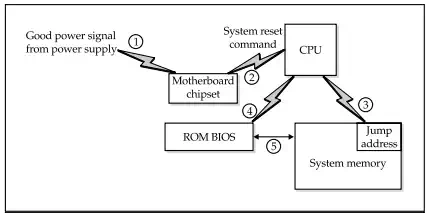
When you flick, push, or pull on the power to your PC, there are absolutely no instructions in memory for the PC to execute. In fact, when the PC is first powered on, it is almost like it is being turned on for the very first time ever. Although it is easy to think of the computer as having a brain and the ability to manage itself, the truth is that it is merely an electrical appliance and must to told what to do at all times. This is especially true at start-up when the power is switched on.
The importance of the PCís BIOS (Basic Input/output System) is that it performs all of the functions the PC needs to get started. The BIOS contains that first instruction the computer needs to get started, programming that checks that computerís hardware is attached and ready, and other routines to help the computer get upand running.
Another of the activities of the BIOS is that it provides the interface that connects the CPU to the input and output devices attached to the PC. The BIOS relieves the PC from needing to know about how hardware devices are attached to the computer. As new hardware is added to the computer, the BIOS eliminates the need for every piece of software in the computer to be updated as to where the hardware and its drivers are located. Only the BIOS configuration data needs to be updated when new equipment is added to the PC, a process usually managed by the BIOS itself without outside intervention required. As illustrated in Figure 6-1, the BIOS services the needs of the CPU, the hardware devices, and the software on the computer. The BIOS and the other functions involved in getting the PC upand running are discussed in this chapter.
An Introduction To The Bios
A PCís BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) includes the programming to perform three vital and useful functions for the PC:
∑ It boots the computer.
∑ It validates the PCís configuration.
∑ It provides an interface between the hardware of the PC and its software.
The BIOS Utilities and Programs
In addition to starting up a PC, the BIOS also contains a collection of programs that are used by an operating system and application software to interact with the hardware, both internal and external, connected to the PC. While operating systems are beginning to include device drivers and utilities of their own to improve performance, most BIOSs contain software for accessing, reading, writing, and moving data between virtually every type of hardware device.
BIOS Manufacturers
The most well-known BIOS manufacturers are Award, AMI (American Megatrends, Inc.), and Phoenix. Like most BIOS manufacturers, these three license their BIOS ROM to motherboard manufacturers who install them on their motherboards and assume the support of the BIOS as well. AMI was once the sole BIOS provider to Intel, the leading motherboard producer. Today, over 80 percent of all motherboards are Intel boards that include a Phoenix BIOS. In 1998, Phoenix purchased Award and now markets the Award BIOS brand under the Phoenix name.