Characteristics Of Computers
The characteristics of computers that have made them so powerful and universally useful are speed, accuracy, diligence, versatility and storage capacity. Let us discuss them briefly
Speed
Computers work at an incredible speed. A powerful computer is capable of performing about 3-4 million simple instructions per second.
Accuracy
In addition to being fast, computers are also accurate. Errors that may occur can almost always be attributed to human error (inaccurate data, poorly designed system or faulty instructions/programs written by the programmer)
Diligence
Unlike human beings, computers are highly consistent. They do not suffer from human traits of boredom and tiredness resulting in lack of concentration. Computers, therefore, are better than human beings in performing voluminous and repetitive jobs.
Versatility
Computers are versatile machines and are capable of performing any task as long as it can be broken down into a series of logical steps. The presence of computers can be seen in almost every sphere – Railway/Air reservation, Banks, Hotels, Weather forecasting and many more.
Storage Capacity
Today’s computers can store large volumes of data. A piece of information once recorded (or stored) in the computer, can never be forgotten and can be retrieved almost instantaneously.
Computer Organization

A computer system (fig.1.1) consists of mainly four basic units; namely input unit, storage unit, central processing unit and output unit. Central Processing unit further includes Arithmetic logic unit and control unit, as shown in Figure 1.2. A computer performs five major operations or functions irrespective of its size and make. These are
· it accepts data or instructions as input,
· it stores data and instruction
· it processes data as per the instructions,
· it controls all operations inside a computer, and
· it gives results in the form of output.
Functional Units:
a. Input Unit: This unit is used for entering data and programs into the computer system by the user for processing.
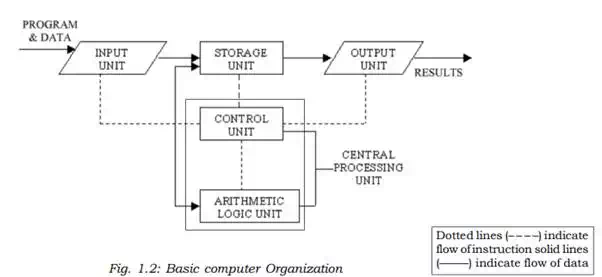
b. Storage Unit: The storage unit is used for storing data and instructions before and after processing.
c. Output Unit: The output unit is used for storing the result as output produced by the computer after processing.
d. Processing: The task of performing operations like arithmetic and logical operations is called processing. The Central Processing Unit (CPU) takes data and instructions from the storage unit and makes all sorts of calculations based on the instructions given and the type of data provided. It is then sent back to the storage unit. CPU includes Arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and control unit (CU)
· Arithmetic Logic Unit: All calculations and comparisons, based on the instructions provided, are carried out within the ALU. It performs arithmetic functions like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and also logical operations like greater than, less than and equal to etc.
· Control Unit: Controlling of all operations like input, processing and output are performed by control unit. It takes care of step by step processing of all operations inside the computer.