Open-End Air Columns
Many musical instruments consist of an air column enclosed
inside of a hollow metal tube. Though the metal tube may be more than a meter
in length, it is often curved upon itself one or more times in order to
conserve space. If the end of the tube is uncovered such that the air at the end of the
tube can freely vibrate when the sound wave reaches it, then the end is
referred to as an open end. If both ends of
the tube are uncovered or open, the musical instrument is said to contain an open-end air
column. A variety of instruments operate on the basis of open-end air columns;
examples include the flute and the recorder. Even some organ pipes serve as
open-end air columns.
Standing
Wave Patterns for the Harmonics
As has already been mentioned, a musical instrument has a set of natural frequencies at which it
vibrates at when a disturbance is introduced into it. These natural frequencies
are known as the harmonics of the instrument; each harmonic is associated with
a standing wave pattern. In Lesson 4 of Unit 10, a standing wave
pattern was defined as a vibrational pattern created within a medium when the
vibrational frequency of the source causes reflected waves from one end of the
medium to interfere with incident waves from the source in such a
manner that specific points along the medium appear to be standing still. In
the case of stringed instruments (discussed earlier), standing wave patterns were drawn to depict the amount of movement of
the string at various locations along its length. Such patterns show nodes -
points of no displacement or movement - at the two fixed ends of the string. In
the case of air columns, a closed end in a column of air is analogous to the
fixed end on a vibrating string. That is, at the closed end of an air column,
air is not free to undergo movement and thus is forced into assuming the nodal
positions of the standing wave pattern. Conversely, air is free to undergo its
back-and-forth longitudinal motion at the open end of an air column; and as
such, the standing wave patterns will depict antinodes at the open ends of air
columns.
So the basis for drawing the standing wave patterns for air
columns is that vibrational antinodes will be present at any open end and
vibrational nodes will be present at any closed end. If this principle is
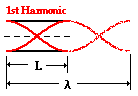
applied to open-end air columns, then the pattern for the fundamental frequency
(the lowest frequency and longest wavelength pattern) will have antinodes at
the two open ends and a single node in between. For this reason, the standing
wave pattern for the fundamental frequency (or first harmonic) for an open-end
air column looks like the diagram below.
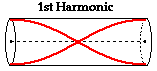
The distance between antinodes on a standing wave pattern is
equivalent to one-half of a wavelength. A careful analysis
of the diagram above shows that adjacent antinodes are positioned at the two
ends of the air column. Thus, the length of the air column is equal to one-half
of the wavelength for the first harmonic.
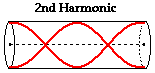
The standing wave pattern for the second harmonic of an
open-end air column could be produced if another antinode and node was added to
the pattern. This would result in a total of three antinodes and two nodes.
This pattern is shown in the diagram below. Observe in the pattern that there
is one full wave in the length of the air column. One full wave is twice the
number of waves that were present in the first harmonic. For this reason, the
frequency of the second harmonic is two times the frequency of the first
harmonic.
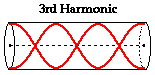
And finally, the standing wave pattern for the third harmonic
of an open-end air column could be produced if still another antinode and node
were added to the pattern. This would result in a total of four antinodes and
three nodes. This pattern is shown in the diagram below. Observe in the pattern
that there are one and one-half waves present in the length of the air column.
One and one-half waves is three times the number of waves that were present in
the first harmonic. For this reason, the frequency of the third harmonic is
three times the frequency of the first harmonic.
Summary
of Length-Wavelength Relationships
The process of adding another antinode and node to each
consecutive harmonic in order to determine the pattern and the resulting
length-wavelength relationship could be continued. If doing so, it is important
to keep antinodes on the open ends of the air column and to maintain an
alternating pattern of nodes and antinodes. When finished, the results should
be consistent with the information in the table below.
The relationships between the standing wave pattern for a
given harmonic and the length-wavelength relationships for open end air columns
are summarized in the table below.
|
Harm. # |
# of Waves in |
# of |
# of Antinodes |
Length- Wavelength Relationship |
|
1 |
1/2 |
1 |
2 |
Wavelength = (2/1)*L |
|
2 |
1 or 2/2 |
2 |
3 |
Wavelength = (2/2)*L |
|
3 |
3/2 |
3 |
4 |
Wavelength = (2/3)*L |
|
4 |
2 or 4/2 |
4 |
5 |
Wavelength = (2/4)*L |
|
5 |
5/2 |
5 |
6 |
Wavelength = (2/5)*L |
Problem-Solving
Scheme
Now the aim of the above discussion is to internalize the
mathematical relationships for open-end air columns in order to perform
calculations predicting the length of air column required to produce a given
natural frequency. And conversely, calculations can be performed to predict the
natural frequencies produced by a known length of air column. Each of these
calculations requires knowledge of the speed of a wave in air (which is
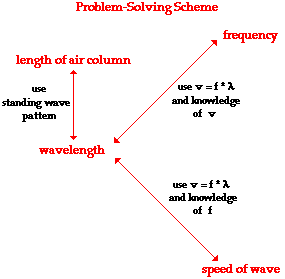
approximately 340 m/s at room temperatures). The graphic below depicts the relationships
between the key variables in such calculations. These relationships will be
used to assist in the solution to problems involving standing waves in musical
instruments.
To demonstrate the use of the above problem-solving scheme,
consider the following example problem and its detailed solution.
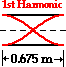
Example Problem #1
The speed of sound waves in air is
found to be 340 m/s. Determine the fundamental frequency (1st harmonic) of an
open-end air column that has a length of 67.5 cm. |
The solution to the problem begins by first identifying known
information, listing the desired quantity, and constructing a diagram of the
situation.
|
Given: v = 340 m/s L = 67.5 cm = 0.675 m |
Find: f1 = ?? |
Diagram:
|
The problem statement asks us to determine the frequency (f)
value. From the graphic above, the only means of finding the frequency is to
use the wave equation (speed = frequency • wavelength) and knowledge of the
speed and wavelength. The speed is given, but wavelength is not known. If the
wavelength could be found then the frequency could be easily calculated. In
this problem (and any problem), knowledge of the length and the harmonic number
allows one to determine the wavelength of the wave. For the first harmonic, the
wavelength is twice the length. This relationship is derived from the diagram
of the standing wave pattern (see table above). The relationship, which works only for the first harmonic of an
open-end air column, is used to calculate the wavelength for this standing wave.
Wavelength = 2 • Length
Wavelength = 2 • 0.675 m
Wavelength = 1.35 m
Now that wavelength is known, it can be combined with the
given value of the speed to calculate the frequency of the first harmonic for
this open-end air column. This calculation is shown below.
speed = frequency • wavelength
frequency = speed /
wavelength
frequency = (340 m/s) /
(1.35 m)
frequency = 252 Hz
Most problems can be solved in a similar manner. It is always
wise to take the extra time needed to set the problem up. Take the time to
write down the given information and the requested information, and to draw a
meaningful diagram.
Seldom in physics are two problems identical. The tendency to
treat every problem the same way is perhaps one of the quickest paths to
failure. It is much better to combine good problem-solving skills (part of
which involves the discipline to set the problem up) with a solid grasp of the
relationships among variables. Avoid the tendency to memorize approaches to
different types of problems.
To further your understanding of these relationships and the
use of the above problem-solving scheme, consider the following example problem and its detailed solution.
Example Problem #2
Determine the length of an open-end air
column required to produce a fundamental frequency (1st harmonic) of 480 Hz.
The speed of waves in air is known to be 340 m/s. |
The solution to the problem begins by first identifying known
information, listing the desired quantity, and constructing a diagram of the
situation.
|
Given: v = 340 m/s f1 = 480 Hz |
Find: L = ?? |
Diagram:
|
The problem statement asks us to determine the length of the
air column. When inspecting the problem-solving scheme described above, one will notice that the only means of finding the length of the air
column is from knowledge of the wavelength. But the wavelength is not known.
However, the frequency and speed are given, so one can use the wave equation
(speed = frequency • wavelength) and knowledge of the speed and frequency to
determine the wavelength. This calculation is shown below.
speed = frequency • wavelength
wavelength = speed
/ frequency
wavelength = (340
m/s) / (480 Hz)
wavelength = 0.708 m
Now that the wavelength is found, the length of the air
column can be calculated. For the first harmonic, the length is one-half the
wavelength. This relationship is derived from the diagram of the standing wave
pattern (see table above). The relationship may also be evident to you by looking at the standing
wave diagram drawn above. This relationship between wavelength and length,
which works only for the first harmonic of an open-end air column, is used to
calculate the wavelength for this standing wave.
Length = (1/2) • Wavelength
Length = (1/2) • Wavelength
Length = 0.354 m
If you have successfully managed the above two problems, take
a try at the following practice problems. As you proceed, be sure to be mindful
of the numerical relationships involved in such problems. And if necessary,
refer to the graphic above.
Check Your Understanding
1. Stan Dinghwaives is
playing his open-end pipe. The frequency of the second harmonic is 880 Hz (a
pitch of A5). The speed of sound through the pipe is 350 m/sec. Find the frequency of the first harmonic and the length
of the pipe.

Answer: 0.398 m
Given:
2nd Harmonic frequency f2 = 880 Hz
v
= 350 m/s
The
length of an air column is related mathematically to the wavelength of the wave
which resonates within it. Thus the strategy for solving for length will be to
first determine the wavelength of the wave using the wave equation and the
knowledge of the frequency and the speed. The wave equation states that v = f •
λ where λ is the wavelength of the wave. For the frequency value, we
could use either 880 Hz for the second harmonic or the 440 Hz value for the
first harmonic. Here, we chose to use the first harmonic value. Rearranging
this equation and substituting allows one to determine the wavelength.
λ = v / f =
(350 m/s) / (440 Hz) = 0.795 m
For
the first harmonic, the length of the air column is one-half the wavelength of
the wave (see Tutorial page). Thus, the following calculation can be performed:
L = 0.5 • λ = 0.398 m
2. On a cold frigid day, Matthew blows on a toy flute,
causing resonating waves in an open-end air column. The speed of sound through
the air column is 336 m/sec. The length of the air column is 30.0 cm. Calculate
the frequency of the first, second, and third harmonics.

Answers: f1 = 560 Hz; f2 = 1120 Hz; f3 = 1680 Hz
Given: v = 336 m/s
L = 30 cm = 0.30 m (use meters for length since the speed is
given in units of meters/s)
The strategy for solving for the frequencies of the first three
harmonics will be to first find the frequency of the first harmonic. The
frequencies of other harmonics are multiples of the first harmonic. The
frequency of the first harmonic can be calculated from the given speed value
and the wavelength. The wavelength is not given but can be calculated from the
length of the air column. For the first harmonic, the wavelength is twice the
length of the air column (see Tutorial page).
Let λ =
wavelength.
λ = 2 • L =
2 • (0.30 m) = 0.60 m
Now rearrange the wave equation v = f • λ to solve for
frequency.
f1 =
v / λ = (336 m/s) / (0.60 m) = 560 Hz
The frequencies of the various harmonics are whole-number
multiples of the frequency of the first harmonic. Each harmonic frequency (fn) is given by the
equation fn = n • f1 where n is
the harmonic number and f1 is the frequency of the first harmonic.
Second
harmonic: f2 =
1120 Hz
Third
harmonic: f3 =
1680 Hz
3. A flute is played with a first harmonic of 196 Hz (a pitch
of G3). The length of the air column is 89.2 cm (quite a long flute). Find the
speed of the wave resonating in the flute.

Answer: 3.50 x 102 m/s (rounded from 349.66 m/s)
Given: L = 89.2 cm = 0.892 m (use meters for length since the speed
is given in order to calculate speed in units of meters/second)
f = 196 Hz (1st
harmonic)
The strategy for solving for the speed of sound will involve
using the wave equation v = f • λ where λ is the wavelength of the
wave. The frequency is stated but the wavelength must be calculated from the
given value of the length of the string. For the first harmonic, the wavelength
is twice the length of the string (see Tutorial page).
λ = 2 • L =
2 • (0.892 m) = 1.784 m
Now substitute into the wave equation to solve for the speed of
the wave.
v = f • λ =
(196 Hz) • (1.784 m)
v = 349.66 m/s =
3.50 x 102 m/s