Application and Practice Questions
Lesson 2 has thus far focused on how to analyse motion
situations using the work and energy relationship. The relationship could be
summarized by the following statements:
|
There is
a relationship between work and mechanical energy change. Whenever work is
done upon an object by an external or nonconservative force, there will be a change in
the total mechanical energy of the object. If only internal forces are doing work (no work done by
external forces), there is no change in total mechanical energy; the total
mechanical energy is said to be "conserved." The quantitative relationship
between work and the two forms of mechanical energy is expressed by the
following equation: KEi + PEi + Wext = KEf + PEf |
Now an effort will be made to apply this relationship to a variety of motion
scenarios in order to test our understanding.
Check Your Understanding
Use your understanding of the work-energy theorem to answer
the following questions. Then click the button to view the answers.
1. Consider the falling and rolling motion of the ball in the
following two resistance-free situations. In one situation, the ball falls off
the top of the platform to the floor. In the other situation, the ball rolls
from the top of the platform along the staircase-like pathway to the floor. For
each situation, indicate what types of forces are doing work upon the ball.
Indicate whether the energy of the ball is conserved and explain why. Finally,
fill in the blanks for the 2-kg ball.
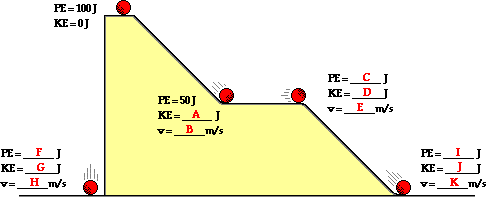

The only force doing work is gravity. Since it is an internal or
conservative force, the total mechanical energy is conserved. Thus, the 100 J
of original mechanical energy is present at each position. So the KE for A
is 50 J.
The PE at the same stairstep is 50 J (C) and thus the KE is
also 50 J
(D).
The PE at zero height is 0 J (F and I). And so the kinetic energy at the bottom of
the hill is 100 J (G and J).
Using the equation KE = 0.5*m*v2, the velocity can be determined to be 7.07 m/s for B and E and 10 m/s for H and K.
The answers
given here for the speed values are presuming that all the kinetic energy of
the ball is in the form of translational kinetic energy. In actuality, some of
the kinetic energy would be in the form of rotational kinetic energy. Thus, the
actual speed values would be slightly less than those indicated. (Rotational
kinetic energy is not discussed here at The Physics Classroom Tutorial.)
2. If frictional forces and air resistance were acting upon
the falling ball in #1 would the kinetic energy of the ball just prior to
striking the ground be more, less, or equal to the value predicted in #1?

The kinetic energy
would be less in a situation that involves friction. Friction would do negative
work and thus remove mechanical energy from the falling ball.
close
Use the following diagram to answer questions #3 - #5.
Neglect the effect of resistance forces.
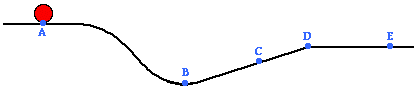
3. As the object moves
from point A to point D across the surface, the sum of its gravitational
potential and kinetic energies ____.
|
a.
decreases, only |
b.
decreases and then increases |
|
c.
increases and then decreases |
d.
remains the same |

The answer
is D. The total mechanical energy
(i.e., the sum of the kinetic and potential energies) is everywhere the same
whenever there are no external or nonconservative forces
(such as friction or air resistance) doing work.
4. The object will have a minimum gravitational potential
energy at point ____.
|
a. A |
b. B |
c. C |
d. D |
e. E |

The answer is B.
Gravitational potential energy depends upon height (PE=m*g*h). The PE is a
minimum when the height is a minimum. Position B is the lowest position in the
diagram.
5. The object's kinetic energy at point C is less than its
kinetic energy at point ____.
|
a. A only |
b. A, D,
and E |
c. B only |
d. D and E |

The answer
is C. Since the total
mechanical energy is conserved, kinetic energy (and thus, speed) will be
greatest when the potential energy is smallest. Point B is the only point that
is lower than point C. The reasoning would follow that point B is the point
with the smallest PE, the greatest KE, and the greatest speed. Therefore, the
object will have less kinetic energy at point C than at point B (only).
6. Many drivers' education
books provide tables that relate a car's braking distance to the speed of the
car (see table below). Utilize what you have learned about the stopping
distance-velocity relationship to complete the table.
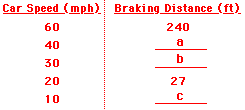

A: 108 ft
Compare 20 mph
to 40 mph - a two-fold increase in speed. A two-fold increase in speed means a
four-fold increase in stopping distance. Multiply 27 by 4.
B: 60 ft
Compare 60 mph
to 30 mph - a two-fold decrease in speed. A two-fold decrease in speed means a four-fold
decrease in stopping distance. Divide 240 by 4.
C: 6.8 ft
Compare 20 mph
to 10 mph - a two-fold decrease in speed. A two-fold decrease in speed means a
four-fold decrease in stopping distance. Divide 27 by 4.
7. Some driver's license exams have the following question.
A
car moving 50 km/hr skids 15 meters with locked brakes. How far will the car
skid with locked brakes if it is moving at 150 km/hr?

The car
skids 135
m. There
is a three-fold increase in the speed of the car (150 / 50 = 3). Thus, there
must be a nine-fold increase in the stopping distance. Multiply 15 meters by 9.
8. Two baseballs are fired into a pile of hay. If one has
twice the speed of the other, how much farther does the faster baseball
penetrate? (Assume that the force of the haystack on the baseballs is constant).

The
faster baseball penetrates four times as
far. When there is a two-fold increase in speed, there is a
four-fold increase in stopping distance. For constant resistance forces,
stopping distance is proportional to the square of the speed.
9. Use the law of conservation of energy (assume no friction)
to fill in the blanks at the various marked positions for a 1000-kg roller
coaster car.
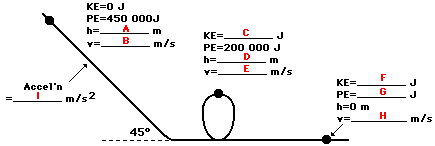

A: h = 45.9 m (from 450 000 =1000*9.8*h)
B: v = 0 m/s (since KE = 0 J)
C: KE = 250 000 J (KE + PE must equal 450 000 J)
D: h = 20.4 m (From 200 000 =1000*9.8*h)
E: v = 22.4 m/s (from 250 000 = 0.5*1000*v^2)
F: KE = 450 000 J (KE + PE must equal 450 000 J)
G: PE = 0 J (since the height is 0 m)
H: v = 31.6 m/s (from 500 000 = 0.5*1000*v^2)
I: a = 7.07 m/s/s (since a = g*sin
angle)
10. If the angle of the initial drop in the roller coaster
diagram above were 60 degrees (and all other factors were kept constant), would
the speed at the bottom of the hill be any different? Explain.

The angle does
not affect the speed at the bottom of the incline. The speed at the bottom of
the incline is dependent upon the initial height of the incline. Many students
believe that a smaller angle means a smaller speed at the bottom. But such
students are confusing speed with acceleration. A smaller angle will lead to a
smaller acceleration along the incline.
11. Determine Li Ping Phar's (a mass of approximately 50 kg) speed at
locations B, C, D and E.
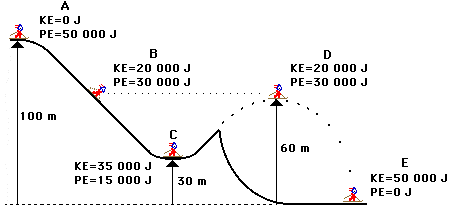

B: KE = 0.5 •m • v2
20 000 J = 0.5 • (50 kg) • v2
v = 28.3 m/s
C: KE = (0.5 •m • v2
35 000 J = 0.5 • (50 kg) • v2
v = 37.4 m/s
D: same as postition B
v = 28.3 m/s
E: KE = 0.5 •m • v2
50 000 J = 0.5 • (50 kg) • v2
v = 44.7 m/s
12. An object which weighs 10 N is dropped from rest from a
height of 4 meters above the ground. When it has free-fallen 1 meter its total
mechanical energy with respect to the ground is ____.
|
a. 2.5 J |
b. 10 J |
c. 30 J |
d. 40 J |

The answer is D.
Energy is conserved in free-fall situations (no external forces
doing work). Thus, the total mechanical energy initially is everywhere the
same. Whatever total mechanical energy (TME) it has initially, it will maintain
throughout the course of its motion. The object begins with 39.2 J of potential
energy (PE = m * g * h = 1 kg * 9.8 m/s/s * 4 m = 39.2 J) and no kinetic
energy. The total mechanical energy (KE + PE) is 39.2 J.
Observe that a
confusion of mass (1 kg) and weight (9.8 N) will inevitably lead to the wrong
answer.
13. During a certain time interval, a 20-N object free-falls
10 meters. The object gains _____ Joules of kinetic energy during this interval.
|
a. 10 |
b. 20 |
c. 200 |
d. 2000 |

The answer is C.
The total amount of mechanical energy is conserved in free-fall
situations (no external forces doing work). Thus, the potential energy that is
lost is transformed into kinetic energy. The object loses 200 J of potential
energy (PE loss = m * g * h where the m•g is 200 N (i.e., the object's weight).
Observe that a
confusion of mass (~20 kg) and weight (200 N) will inevitably lead to the wrong
answer.
14. A rope is attached to a 50.0-kg crate to pull it up a
frictionless incline at constant speed to a height of 3-meters. A diagram of
the situation and a free-body diagram are shown below. Note that the force of
gravity has two components (parallel and perpendicular component); the parallel
component balances the applied force and the perpendicular component balances
the normal force.
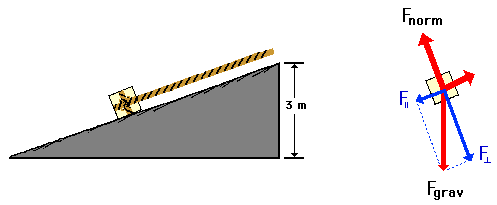
Of the forces acting upon the crate, which one(s) do work
upon it?

Both gravity and
applied forces do work. The normal force does not do work
since the angle between Fnorm and
the displacement is 90 degrees. (If necessary, review the lesson on work.)
close
Based upon the types of forces acting upon the system and
their classification as internal or external forces, is energy conserved?
Explain.

No!
The applied force
is an external or nonconservative force.
And since it does work, the total mechanical energy is not conserved.
close
Calculate the amount of work done upon the crate.

Wext = 1470 J
Start with TMEi + Wext = TMEf
KEi + PEi + Wext = KEf + PEf
KEi + 0 J + Wext = KEf +
(50 kg) * (9.8 m/s/s) * (3 m)
(KEi = KEf since speed is constant. Thus, both KE
terms can be eliminated from the equation.)
Wext = (50 kg) * (9.8
m/s/s) * (3 m) = 1470 J