The Centripetal Force Requirement
An object moving in a circle is experiencing an acceleration.
Even if moving around the perimeter of the circle with a constant speed, there
is still a change in velocity and subsequently an acceleration. This
acceleration is directed towards the center of the circle. And in accord with Newton's
second law of motion, an object which experiences an acceleration
must also be experiencing a net force. The direction of the net force is in the
same direction as the acceleration. So for an object moving in a circle, there
must be an inward force acting upon it in order to cause its inward
acceleration. This is sometimes referred to as the centripetal
force requirement. The word centripetal (not to be
confused with the F-word centrifugal)
means center seeking. For object's moving in circular motion, there is a net
force acting towards the center which causes the object to seek the center.
To understand the importance of a centripetal force, it is
important to have a sturdy understanding of the Newton's first law of motion - the law of inertia. The law of inertia states that ...
|
... objects in motion tend to stay in motion with the
same speed and the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. |
According to Newton's first law of motion, it is the natural
tendency of all moving objects to continue in motion in the same direction that
they are moving ... unless some form of unbalanced force acts upon the object
to deviate its motion from its straight-line path. Moving objects will tend to
naturally travel in straight lines; an unbalanced force is only required to
cause it to turn. Thus, the presence of an unbalanced force is required for
objects to move in circles.
Inertia,
Force and Acceleration for an Automobile Passenger
The idea expressed by Newton's law of inertia should not be
surprising to us. We experience this phenomenon of inertia nearly every day
when we drive our automobile. For example, imagine that you are a passenger in
a car at a traffic light. The light turns green and the driver accelerates from
rest. The car begins to accelerate forward, yet relative to the seat which you
are on your body begins to lean backwards. Your body being at rest tends to
stay at rest. This is one aspect of the law of inertia - "objects at rest
tend to stay at rest." As the wheels of the car spin to generate a forward
force upon the car and cause a forward acceleration, your body tends to stay in
place. It certainly might seem to you as though your body were experiencing a
backwards force causing it to accelerate backwards. Yet you would have a
difficult time identifying such a backwards force on your body. Indeed there
isn't one. The feeling of being thrown backwards is merely the tendency of your
body to resist the acceleration and to remain in its state of rest. The car is
accelerating out from under your body, leaving you with the false feeling of
being pushed backwards.
Now imagine that you are in the same car moving along at a
constant speed approaching a stoplight. The driver applies the brakes, the
wheels of the car lock, and the car begins to skid to a stop. There is a
backwards force upon the forward moving car and subsequently a backwards
acceleration on the car. However, your body, being in motion, tends to continue
in motion while the car is skidding to a stop. It certainly might seem to you
as though your body were experiencing a forwards force causing it to accelerate
forwards. Yet you would once more have a difficult time identifying such a
forwards force on your body. Indeed there is no physical object accelerating
you forwards. The feeling of being thrown forwards is merely the tendency of
your body to resist the deceleration and to remain in its state of forward
motion. This is the second aspect of Newton's law of inertia - "an object
in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction... ." The unbalanced force acting upon the car
causes the car to slow down while your body continues in its forward motion.
You are once more left with the false feeling of being pushed in a direction
which is opposite your acceleration.
These two driving scenarios are summarized by the following
graphic.

In each case - the car starting from rest and the moving car
braking to a stop - the direction which the passengers lean is opposite the
direction of the acceleration. This is merely the result of the passenger's inertia
- the tendency to resist acceleration. The passenger's lean is not an
acceleration in itself but rather the tendency to maintain the state of motion
while the car does the acceleration. The tendency of a passenger's body to
maintain its state of rest or motion while the surroundings (the car)
accelerate is often misconstrued as an acceleration. This becomes particularly
problematic when we consider the third possible inertia experience of a
passenger in a moving automobile - the left hand turn.
Suppose that on the next part of your travels the driver of
the car makes a sharp turn to the left at constant speed. During the turn, the
car travels in a circular-type path. That is, the car 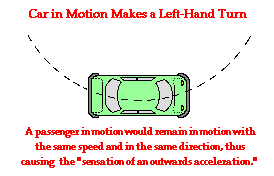 sweeps out one-quarter of a circle. The friction force acting upon the
turned wheels of the car causes an unbalanced force upon the car and a
subsequent acceleration. The unbalanced force and the acceleration are both
directed towards the center of the circle about which the car is turning. Your body however is
in motion and tends to stay in motion. It is the inertia of your body - the
tendency to resist acceleration - that causes it to continue in its forward
motion. While the car is accelerating inward, you continue in a straight line.
If you are sitting on the passenger side of the car, then eventually the
outside door of the car will hit you as the car turns inward. This phenomenon
might cause you to think that you are being accelerated outwards away from thecenter of
the circle. In reality, you are continuing in your straight-line inertial path
tangent to the circle while the car is accelerating out from under you. The
sensation of an outward force and an outward acceleration is a false sensation.
There is no physical object capable of pushing you outwards. You are merely
experiencing the tendency of your body to continue in its path tangent to the
circular path along which the car is turning. You are once more left with the
false feeling of being pushed in a direction that is opposite your acceleration.
sweeps out one-quarter of a circle. The friction force acting upon the
turned wheels of the car causes an unbalanced force upon the car and a
subsequent acceleration. The unbalanced force and the acceleration are both
directed towards the center of the circle about which the car is turning. Your body however is
in motion and tends to stay in motion. It is the inertia of your body - the
tendency to resist acceleration - that causes it to continue in its forward
motion. While the car is accelerating inward, you continue in a straight line.
If you are sitting on the passenger side of the car, then eventually the
outside door of the car will hit you as the car turns inward. This phenomenon
might cause you to think that you are being accelerated outwards away from thecenter of
the circle. In reality, you are continuing in your straight-line inertial path
tangent to the circle while the car is accelerating out from under you. The
sensation of an outward force and an outward acceleration is a false sensation.
There is no physical object capable of pushing you outwards. You are merely
experiencing the tendency of your body to continue in its path tangent to the
circular path along which the car is turning. You are once more left with the
false feeling of being pushed in a direction that is opposite your acceleration.
The
Centripetal Force and Direction Change
Any object moving in a circle (or along a circular path)
experiences a centripetal force. That is, there is some
physical force pushing or pulling the object towards the center of
the circle. This is the centripetal force requirement. The word centripetal is merely
an adjective used to describe the direction of the force. We are not
introducing a new type of force
but rather describing the direction of the net force acting upon the object
that moves in the circle. Whatever the object, if it moves in a circle, there
is some force acting upon it to cause it to deviate from its straight-line
path, accelerate inwards and move along a circular path. Three such examples of
centripetal force are shown below.
|
|
|
|
|
As a car
makes a turn, the force of friction acting upon the turned wheels of the car
provides centripetal force required for circular motion. |
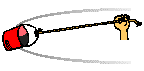
As a
bucket of water is tied to a string and spun in a circle, the tension force
acting upon the bucket provides the centripetal force required for circular
motion. |
As the
moon orbits the Earth, the force of gravity acting upon the moon provides the
centripetal force required for circular motion. |
The centripetal force for uniform circular motion alters the
direction of the object without altering its speed. The idea that an unbalanced
force can change the direction of the velocity vector but not its magnitude may
seem a bit strange. How could that be? There are a number of ways to approach
this question. One approach involves to analyze the motion from a work-energy standpoint. that work is a force acting
upon an object to cause a displacement. The amount of
work done upon an object is found using the equation
Work = Force * displacement * cosine (Theta)
where the Theta in the
equation represents the angle between the force and the displacement. As the
centripetal force acts upon an object moving in a circle at constant speed, the
force always acts inward as the velocity of the object is directed tangent to
the circle. This would mean that the force is always directed perpendicular to
the direction that the object is being displaced. The angle Theta in the above
equation is 90 degrees and the cosine of 90 degrees is 0. Thus, the work done
by the centripetal force in the case of uniform circular motion is 0
Joules. that when no work is done upon an
object by external forces, the total mechanical energy (potential energy plus
kinetic energy) of the object remains constant. So if an object is moving in a
horizontal circle at constant speed, the centripetal force does not do work and
cannot alter the total mechanical energy of the object. For this reason, the
kinetic energy and therefore, the speed of the object will remain constant. The
force can indeed accelerate the object - by changing its direction - but it
cannot change its speed. In fact, whenever the unbalanced centripetal force
acts perpendicular to the direction of motion, the speed of the object will
remain constant. For an unbalanced force to change the speed of the object,
there would have to be a component of force in the direction of (or the
opposite direction of) the motion of the object.
Applying Vector Components and Newton's Second Law
A second approach to this question of why the centripetal
force causes a direction change but not a speed change involves vector
components and Newton's second law. The following imaginary
scenario will be used to help illustrate the point.
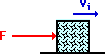
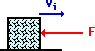
 Suppose at the local ice factory, a block of ice slides out of the
freezer and a mechanical arm exerts a force to accelerate it across the icy,
friction free surface. Last week, the mechanical arm was malfunctioning and
exerting pushes in a randomly directed fashion. The various direction of forces
applied to the moving block of ice are shown below. For each case, observe the
force in comparison to the direction of motion of the ice block and predict
whether the force will speed up, slow down or not affect the speed of the
block. Use vector components to make your predictions. Then check your answers
by clicking on the button.
Suppose at the local ice factory, a block of ice slides out of the
freezer and a mechanical arm exerts a force to accelerate it across the icy,
friction free surface. Last week, the mechanical arm was malfunctioning and
exerting pushes in a randomly directed fashion. The various direction of forces
applied to the moving block of ice are shown below. For each case, observe the
force in comparison to the direction of motion of the ice block and predict
whether the force will speed up, slow down or not affect the speed of the
block. Use vector components to make your predictions. Then check your answers
by clicking on the button.
|
|
Physical Situation |
Speed up, slow down or not
affect the speed? |
Explanation |
|
a. |
|
Increases Speed |
There is an unbalanced
force in the same direction as the block's motion. A force exerted in the
direction of motion will cause an increase in speed. |
|
b. |
|
Decreases Speed |
There is an unbalanced
force in the opposite direction as the block's motion. A force directed
opposite an object's motion will cause a decrease in speed. |
|
c. |
|
Increases Speed close |
This unbalanced force has
two components - one is downward and the other is rightward. Downward
components of force cannot alter rightward speeds. But a rightward component
of force would increase the rightward speed. A component of force exerted in
the direction of motion will cause an increase in speed. |
|
d. |
|
Increases Speed |
This
unbalanced force has two components - one is downward and the other is
rightward. Downward components of force cannot alter rightward speeds. But a
rightward component of force would increase the rightward speed. A component
of force exerted in the direction of motion will cause an increase in speed. close |
|
e. |
|
No affect on speed. |
There is no component of
force in the direction of the motion. Thus, the object will neither speed up
nor slow down. This downward component of force will only be counteracted by
a greater normal force of the ground pushing up on the block. To change the
speed of a moving object, there must be a component of force in the same
direction or the opposite direction as the motion. |
The examples above illustrate that a force is only capable of
slowing down or speeding up an object when there is a component directed in the
same direction or opposite direction as the motion of the object. In case e,
the vertical force does not alter the horizontal motion. It is sometimes said
that perpendicular components of motion are independent of each other. A
vertical force cannot affect a horizontal motion.
To summarize, an object in uniform circular motion
experiences an inward net force. This inward force is sometimes referred to as
a centripetal force, where centripetal describes
its direction. Without this centripetal force, an object could never alter its
direction. The fact that the centripetal force is directed perpendicular to the
tangential velocity means that the force can alter the direction of the
object's velocity vector without altering its magnitude.
Check Your Understanding
 For questions #1-#5: An object is moving in a clockwise direction
around a circle at constant speed. Use your understanding of the concepts of velocity, acceleration and force to answer the next five questions.
Use the diagram shown at the right. Click the button to check your answers.
For questions #1-#5: An object is moving in a clockwise direction
around a circle at constant speed. Use your understanding of the concepts of velocity, acceleration and force to answer the next five questions.
Use the diagram shown at the right. Click the button to check your answers.
1. Which vector below represents the direction of the force
vector when the object is located at point A on the circle?
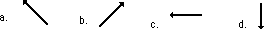
2. Which vector below represents the direction of the force
vector when the object is located at point C on the circle?
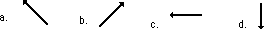
3. Which vector below represents the direction of the
velocity vector when the object is located at point B on the circle?
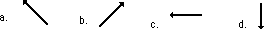
4. Which vector below represents the direction of the
velocity vector when the object is located at point C on the circle?
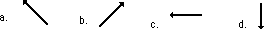
5. Which vector below represents the direction of the
acceleration vector when the object is located at point B on the circle?
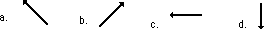

1. Answer = D
The force vector is directed inward to the circle; that would be
downward when at point A
2. Answer = B
The force vector is directed inwards; that would be up and to
the right when the object is at point C.
3. Answer = D
The velocity vector is directed tangent to the circle; that
would be downwards when at point B.
4. Answer = A
The velocity is directed tangentially; that would be upwards and
leftwards when at point C.
5. Answer = C
The acceleration
would be directed inwards; that would be leftwards when the object is at point
B.
6. Rex Things and Doris Locked are out on a date. Rex makes a
rapid right-hand turn. Doris begins sliding across the vinyl seat (that Rex had
waxed and polished beforehand) and collides with Rex. To break the awkwardness
of the situation, Rex and Doris begin discussing the physics of the motion that
was just experienced. Rex suggests that objects which move in a circle
experience an outward force. Thus, as the turn was made, Doris experienced an
outward force that pushed her towards Rex. Doris disagrees, arguing that
objects that move in a circle experience an inward force. In this case,
according to Doris, Rex traveled in a circle due to the force of his door pushing him inward. Doris
did not travel in a circle since there was no force pushing her inward; she
merely continued in a straight line until she collided with Rex. Who is
correct? Argue one of these two positions.

Doris is correct.
When the turn is
made, Doris continues in a straight-line path; this is Newton's first law of motion.
Once Doris collides with Rex, there is then an unbalanced force capable of
accelerating Doris towards the center center of the circle, causing the circular motion.
7. Kara Lott is practicing winter driving in the GBS parking
lot. Kara turns the wheel to make a left-hand turn but her car continues in a
straight line across the ice. Teacher A and Teacher B had viewed the
phenomenon. Teacher A argues that the lack of a frictional force between the
tires and the ice results in a balance of forces that keeps the car traveling
in a straight line. Teacher B argues that the ice placed an outward force on
the tire to balance the turning force and thus keep the car traveling in a
straight line. Which teacher is (A or B) is the physics teacher? ______ Explain
the fallacy in the other teacher's argument.

Teacher A is correct (and is hopefully the
physics teacher).
A car turns in a
circle due to the friction against its turned wheels. With wheels turned and no
friction, there would be no circle. That is the problem in this situation.