Real-World Applications
In
a collision, an object experiences a force for a given amount of time that results in its massundergoing a change in velocity (i.e., that results in a momentum
change).
There are four physical quantities mentioned in the above
statement - force, time, mass, and velocity change. The force multiplied by the
time is known as the impulse and the mass multiplied by the velocity change is
known as the change in momentum. The impulse experienced by an object is always
equal to the change in its momentum. In terms of equations, this was expressed
as
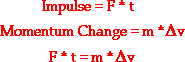
This is known as the impulse-momentum change theorem.
 In this part of Lesson 1, we will examine some real-world applications
of the impulse-momentum change theorem. We will examine some physics in action
in the real world. In particular, we will focus upon
In this part of Lesson 1, we will examine some real-world applications
of the impulse-momentum change theorem. We will examine some physics in action
in the real world. In particular, we will focus upon
· the effect
of collision time upon the
amount of force an object experiences, and
· the effect of rebounding upon the velocity change and
hence the amount of force an object experiences.
As an effort is made to apply the impulse-momentum change
theorem to a variety of real-world situations, keep in mind that the goal is to
use the equation as a guide to thinking about how an alteration in the value of
one variable might affect the value of another variable.