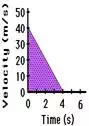
Calculating the Area of a Triangle
Now we will look at a few example computations of the area
for a few triangles. The solution for finding the area is shown for the first
example below. The shaded triangle on the velocity-time graph has a base of 4
seconds and a height of 40 m/s. Since the area of triangle is found by using
the formula A = ½ * b * h, the area is ½ * (4 s) * (40 m/s) = 80 m. That is,
the object was displaced 80 meters during the four seconds of motion.
|
|
Area = ½ * b * h |
 Now try the following two practice problems as a check of your
understanding. Determine the displacement of the object during the first second
(Practice A) and during the first 3 seconds (Practice B).
Now try the following two practice problems as a check of your
understanding. Determine the displacement of the object during the first second
(Practice A) and during the first 3 seconds (Practice B).
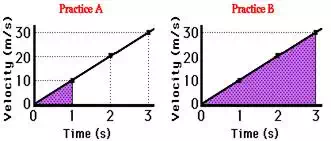

The area of a triangle is given by the equation
Area = ½ • b • h
where b = 1 s and h = 10 m/s
Area = ½ • (1 s)
• (10 m/s) = 5 m
That is, the
object was displaced 5 m during the first second of motion.

The area of a triangle is given by the equation
Area = ½ • b • h
where b = 3 s and h = 30 m/s
Area = ½ • (3 s)
• (30 m/s) = 45 m
That is, the
object was displaced 45 m during the first second of motion.