The Meaning of Slope for a p-t Graph
As discussed in the previous part of Lesson
3, the slope of a position vs. time graph reveals pertinent information about
an object's velocity. For example, a small slope means a small velocity; a
negative slope means a negative velocity; a constant slope (straight line)
means a constant velocity; a changing slope (curved line) means a changing
velocity. Thus the shape of the line on the graph (straight, curving, steeply
sloped, mildly sloped, etc.) is descriptive of the object's motion. In this
part of the lesson, we will examine how the actual slope value of any straight
line on a graph is the velocity of the object.
Consider a car moving with a constant velocity of +10 m/s for
5 seconds. The diagram below depicts such a motion.
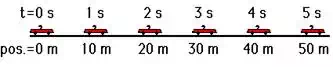
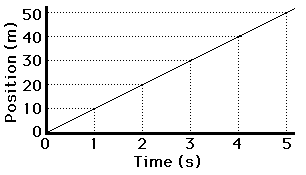 The position-time graph would look like the graph at the right. Note
that during the first 5 seconds, the line on the graph slopes up 10 m for every
1 second along the horizontal (time) axis. That is, the slope of the line is
+10 meter/1 second. In this case, the slope of the line (10 m/s) is obviously
equal to the velocity of the car. We will examine a few other graphs to see if
this a principle that is true of all position vs. time graphs.
The position-time graph would look like the graph at the right. Note
that during the first 5 seconds, the line on the graph slopes up 10 m for every
1 second along the horizontal (time) axis. That is, the slope of the line is
+10 meter/1 second. In this case, the slope of the line (10 m/s) is obviously
equal to the velocity of the car. We will examine a few other graphs to see if
this a principle that is true of all position vs. time graphs.
Now consider a car moving at a constant velocity of +5 m/s
for 5 seconds, abruptly stopping, and then remaining at rest (v = 0 m/s) for 5
seconds.
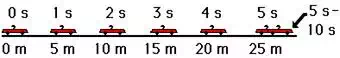
 If the position-time data for such a car were graphed, then the
resulting graph would look like the graph at the right. For the first five
seconds the line on the graph slopes up 5 meters for every 1 second along the
horizontal (time) axis. That is, the line on the position vs. time graph has a
slope of +5 meters/1 second for the first five seconds. Thus, the slope of the
line on the graph equals the velocity of the car. During the last 5 seconds (5
to 10 seconds), the line slopes up 0 meters. That is, the slope of the line is
0 m/s - the same as the velocity during this time interval.
If the position-time data for such a car were graphed, then the
resulting graph would look like the graph at the right. For the first five
seconds the line on the graph slopes up 5 meters for every 1 second along the
horizontal (time) axis. That is, the line on the position vs. time graph has a
slope of +5 meters/1 second for the first five seconds. Thus, the slope of the
line on the graph equals the velocity of the car. During the last 5 seconds (5
to 10 seconds), the line slopes up 0 meters. That is, the slope of the line is
0 m/s - the same as the velocity during this time interval.
 Both of these examples reveal an important principle. The principle is
that the slope of the line on a position-time graph is equal to the velocity of
the object. If the object is moving with a velocity of +4 m/s, then the slope
of the line will be +4 m/s. If the object is moving with a velocity of -8 m/s,
then the slope of the line will be -8 m/s. If the object has a velocity of 0
m/s, then the slope of the line will be 0 m/s.
Both of these examples reveal an important principle. The principle is
that the slope of the line on a position-time graph is equal to the velocity of
the object. If the object is moving with a velocity of +4 m/s, then the slope
of the line will be +4 m/s. If the object is moving with a velocity of -8 m/s,
then the slope of the line will be -8 m/s. If the object has a velocity of 0
m/s, then the slope of the line will be 0 m/s.
