Spontaneous & Stimulated Emission
Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation
Light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation is a phrase that may not be familiar to you, but you have certainly used the acronym for this phrase countless times: laser. In this lesson, we discuss the fundamental process underlying lasers, or stimulated emission. But, first, we will discuss two related concepts: absorption and spontaneous emission.
Please note that in this lesson, when the term radiation is mentioned, it is in reference to electromagnetic radiation and not particulate radiation. Recall that visible light, as well as any other segment of the electromagnetic spectrum, is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Also, recall that the term photon is used to refer to a 'packet' of electromagnetic radiation.
|
|
|
Visible Laser Light |
Absorption
Absorption, spontaneous emission, and stimulated emission are all processes that deal with orbital electrons and photons. Note that these atomic interactions are not always solely confined to electrons, but to simplify our discussion, we will focus on electrons. If a photon interacts with an orbital electron, given the appropriate conditions, the photon is absorbed by the electron. When this occurs the electron moves to a higher energy level. Such an event is called absorption. When an electron moves to a higher energy level it is said to be in an excited state.
|
|
|
Absorption |
Spontaneous Emission
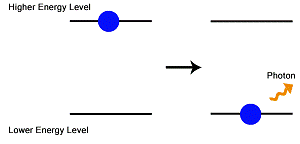
Spontaneous emission occurs when an electron that is in an excited state spontaneously transitions to a lower energy state. When this occurs, a photon is emitted. The energy of the photon is equal to the energy difference between the two energy levels. All forms of luminescence are the result of spontaneous emissions of light, which means that the entertaining glow-in-the-dark phenomena is also the result of spontaneous emissions of light.
|
|
|
Spontaneous |
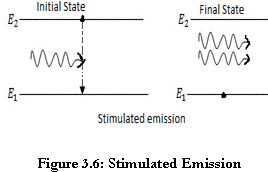
Differentiate between spontaneous and stimulated emissions.
|
SR No |
Spontaneous emission |
Stimulated emission |
|
1 |
The transition of an electron from the excited state to the ground state happens as a result of the natural tendency of the electron without the action of any external agent. The radiation produced as a result of such transitions is called as spontaneous radiation. |
Stimulated emission of radiation is the process whereby photons are used to generate other photons that have exact phase and wavelength as that of parent photon. |
|
2 |
This phenomenon is found in LEDs, Fluorescent tubes. |
This is the key process of formation of laser beam. |
|
3 |
There is no population inversion of electrons in LEDs. |
Population inversion is achieved by various ‘pumping’ techniques to get amplification giving the LASER its name “Light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation.” |
|
4 |
No external stimuli required. |
Thus stimulated emission is caused by external stimuli. |
|
5 |
|
|