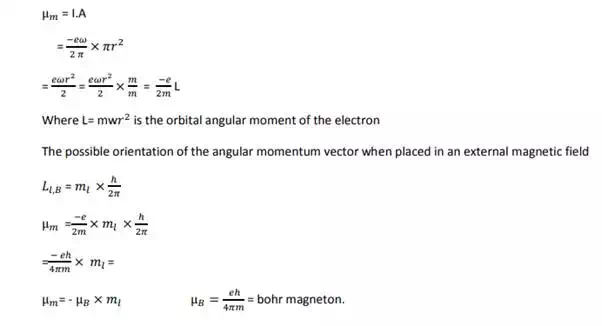
Hysteresis
lagging of magnetization (B) behind the magnetizing field (H) is called hysteresis.
Hysteresis loss: It is the loss of energy in taking a ferromagnetic body through a complete cycle of magnetization and this loss is represented by the area enclosed by the hysteresis loop.
Hard and soft magnetic materials: Based on the area of hysteresis, magnetic materials can be classified into hard and soft magnetic materials.
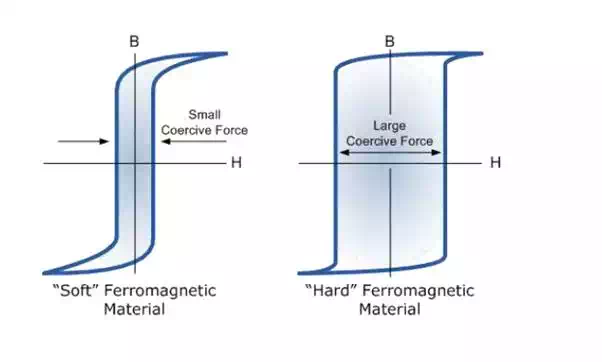

is difficult because of presence of impurities vely easier .even for small changes in the magnetizing and crystal imperfection and it is irreversible field magnetization changes by large amount. in nature (iii) The coercitivity and retentivity are large
(iii) )the coercitivity and retentivity aresmall .these Hence these materials cannot be easily magne- materials can be easily magnetized and demagnetized.

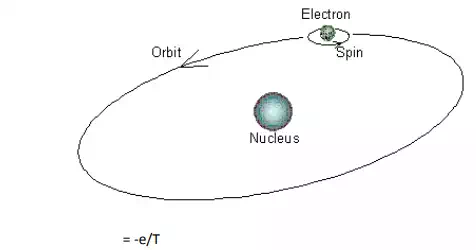
Origin of magnetic moment.
In atoms the permanent magnetic moments can arises due to the following.
1 the orbital magnetic moment of the electrons
2 the spin magnetic moment of the electrons.
3 the spin magnetic moment of nucleus.
Orbital magnetic moment of the electrons and bohr magneton:
We know that in an atom electrons revolve round the nucleus in different circular orbits. Let m be the mass of the electron and r the radius of the orbit in which it moves with angular velocity w
We can calculate the electric current due to the moving electron.
Current I=charge flow/unit time
Where T is the time taken for one revolution
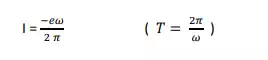
We know that the current flowing through a circular coil produces a magnetic field in a direction perpendicular to the area of the coil and it is identical to a magnetic moment produced by such a dipole is