Classification of magnetic materials:
By the application of magnetic field some materials will not show any effect that are called nonmagnetic materials and those which show some effects are called magnetic materials
All magnetic materials magnetized in an applied external magnetic field.
Depending on the direction and magnitude of magnetization and also the effect of temperature on magnetic properties, all magnetic materials are classified into dia,para and ferromagnetic materials.
Two more classes of material have structure very close to ferro magnetic materials, but posses quiet different magnetic properties. They are anti-ferro magnetic and ferromagnetic materials.
Diamagnetism:
The number of orientations of electronic orbits in an atom be such that vectoe sum of magnetic moment is zero
The external field will cause a rotation action on the individual electronic orbits this produces an induced magnetic moment which is in the direction opposite to the field and hence tenda to decrease the magnetic induction present in the substance.Thus the diamagnetic is the phenomena by which the induced magnetic moment is always in the opposite direction of the applied field.
Properties of diamagnetic materials
1. Diamagnetic material get magnetized in a direction opposite to the magnetic field.
2. Weak repulsion is the characteristic of diamagnetism
3. permanent dipoles are absent
4. Relative permeability is less than one but positive
5. The magnetic susceptibility is negative and small.It is not effected by temperature.
6. Diamagnetism is universal i.e all materials when exposed to external magnetic fields,tend to develop magnetic moments opposite in the direction to the applied field.
7. When placed inside a magnetic field, magnetic lines of force are replaced as
Paramagnetism
The number of orientations of orbital and spin magnetic moments be such that he vector sum of magnetic moment is not zero and there is a resultant magnetic moment in each atom even in the absence of applied field.
The net magnetic moments of the atoms are arranged in random directions because of thermal fluctuations ,in the absence of external magnetic field. Hence there is no magnetization.
If we apply the external magnetic field there is an enormous magnetic moment along the field direction and the magnetic induction will be increase. Thus induced magnetism is the source of paramagnetism.
Properties of paramagnetism materials:
1. paramagnetic materials get magnetized in the direction of the magnetic field.
2. Weak attraction is characteristic of paramagnetism
3. paramagnetic material posses permanent magnetic dipoles.
4. Relative permeability is greater than one but small i.e this indicate that when paramagnetic substance is placed in a uniform magnetic field the field inside the material will be more than the applied field.
5. The magnetic susceptibility is small and positive the magnetic susceptibility of paramagnetic is inversely proportional to absolute temperature i.e x=C/T this is called curie law ,c is called curie constant
6. Paramagnetic susceptibility is independent of the applied field strength.
7. Spin alignment is random
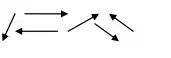
Ferromagnetism:
Ferromagnetism arises when the magnetic moments of adjacent atoms are arranged in a regular order i.e all pointing in the same direction .The ferromagnetic substance thus possess a magnetic moment even in the absence of the applied magnetic field ,this magnetization is known as the spontaneous magnetization
There is a special form of interaction called “exchange “coupling occurring between adjacent atoms ,coupling their magnetic moment together in rigid parallelism.
Properties of ferromagnetic materials
1. In ferromagnetism materials, large magnetization occurs in the direction of the field.
2. Strong attraction is the characteristic of ferromagnetism.
3. They possess spontaneous magnetization.
4. The relative permeability is very high for Ferro magnetic.
5. The magnetic susceptibility is positive and very high.
6. Magnetic susceptibility is fairly high and constant up to a certain temperature according the equation

7 . Ferromagnetism is due to the existence of magnetic domains which can be spontaneously magnetized.
8 . Exhibit hysteresis.
9 . Spin alignment is parallel in the same direction 1
10 . When placed inside a magnetic field it attracts the magnetic lines of forces very strongly
11 . Permanent and electro magnetic are made using ferromagnetic materials.
12 . Example iron, nickel, cobalt.
Antiferro magnetism
Anti-ferromagnetism arises when the spin magnetic moment of neighbouring atoms are oriented in an antiparallel order
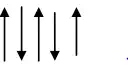
In the absence of external magnetic field the magnetization of anti-ferro magnetic specimen will be zero, because of anti-parallel and equal spin magnetic moment.
By the application of the external magnetic field a small magnetization in the direction of the applied magnetic field takes place this magnetization varies with temperature as shown

At neel temperature the magnetization or susceptibility is maximum and above it the magnetization decreases with increasing temperature according to the relation

The decrease of magnetization with an increase of temperature is a property of of the paramagnetic substance, therefore the specimen becomes paramagnetic above
Examples Mno,Nio,Feo,Mns etc