Dielectric Properties
Dielectrics are non-metallic materials of high specific resistance, negative temperature coefficient of resistance and large insulation resistance.
Dielectrics are of two types
(i) Polar dielectrics
(ii) Non polar dielectrics
(i) Polar dielectrics: these dielectric molecules will not have centre of symmetry here the centers of positive and negative charges will not coincide and hence it possess a net dipole moment in it.
Ex: H2o, N2o, Hcl
Effect of electric field:
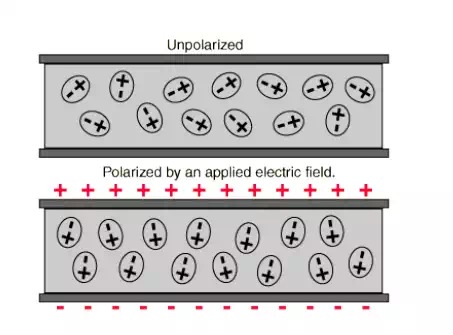
In the absence of electric field: in the absence of electric field the polar dielectric molecules themselves posses some dipole moment .but since these dipole are randomly oriented they cancel each other and the net dipole moment will be very very less
In the presence of electric field: now when an external electric field is applied to the polar dielectric molecule the dipole will align themselves parallel to the field direction and produce a net dipole moment.
(ii) Non polar dielectricss: these dielectric molecule posses centre of symmetry and hence the centres of positive and negative charges coincide. Therefore the net charges and net dipole moment of these molecule will be zero hence these non-polar molecules will not possess any dipole moment in it.
Ex: N2, H2, O2, CO2
Effect of electric field: when non-polar molecule is placed in an external electric field a force is exerted on each charge particle within the molecule i.e. the positive charges are pushed along the field direction and the negative charges are pushed opposite to the filed direction. Hence the positive and negative charges separated by some distance from their equilibrium position, creating a dipole and therefore net dipole moment will be produced in non-polar molecule.
Electric dipole:two equal and opposite charges small in magnitude and separated by a small distance constitute a electric dipole.
Dipole moment: if two charges +q and –q are separated by a distance l than the dipole moment can be defined as product of magnitude of charges and distance between them. µ =q.l
· it is a vector quantity
· the direction of µ is from negative to positive
Dielectric constant : dielectric constant is the ratio between the permittivity of the medium and the permittivity of the free space
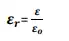
· since it is the ratio of same quantity has no units
Electric polarization : let us consider an atom placed inside an electric field the centre of positive charge is displaced along the applied field direction while the centre of negative charge is displaced in the opposite direction. Thus a dipole is produced when a dielectric material is placed inside an electric field such dipoles are created .
This process of producing electric dipoles which are oriented along the field direction is called polarization in dielectrics.