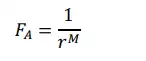Crystal structure
A solid is a group of atoms, ions or
molecules possessing definite shape and volume. When a solid is subjected to
forces (shearing forces),it resists the forces and under goes deformation.
After removing the forces it regains its shape and volume. Such properties are
not exhibited by liquids or gases.
The properties and performance of every engineering material depends on
internal structure. .mechanical properties determine the behaviour of
engineering materials under applied forces and loads. The response of the
material to applied force depends on the type of bonding, structural
arrangement of atoms or molecules and type of number of imperfections,
sensitive to manufacturing process and operations. (Stress, strain,
brittleness, ductility, fatigue, toughness)
The atoms in solids have two types of energies
(a) Potential energy
(b) Kinetic energy
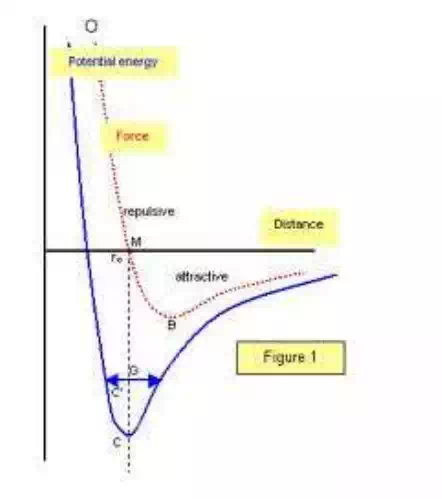
When the atoms are in free state (separated by infinite distance) then the potential energy becomes zero. And the P.E is inversely related to some power of distance of separation.
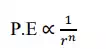
The P.E due to attraction is –ve; as the atoms do work of attraction. The P.E due to repulsion is + ve; as the external work is done to bring the atoms together.
BONDING: the process of holding the atoms together the attractive and repulsive forces that tend to hold the adjacent atoms together at a particular distance in order to balance the opposite forces.
Nature of bonding forces:
To understand the nature of bonding forces, consider a system of two atoms. These two atoms exert attractive and repulsive forces on each other, such that the bonding force is „F‟
When the two atoms are present at distance of separation of „r‟,
then the attractive force „FA‟ is given by