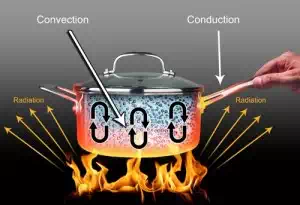
Modes of Heat Transfer – Conduction, Convection & Radiation
Heat is a
form of energy which transfers between bodies which are kept under thermal
interactions. When a temperature difference occurs between two bodies or a body
with its surroundings, heat transfer occurs. In this article, we are going to
deal with the different modes of heat transfer. Heat transfer occurs basically
in three modes:
1. Conduction
2. Convection and
3. Radiation
CONDUCTION:
Conduction is
the mode of heat transfer occurs from one part of a substance to another part
of within the substance itself or with another substance which is placed in
physical contact. In conduction, there is no noticeable movement of molecules.
You might be think that then how this heat transfer occurs? The heat transfer
occurs here by the two mechanisms happen.
1. By the transfer of free
electrons. (Good conductors like metals have a plenty of free electrons to make
conductive heat transfer.
2. The atoms and molecules
having energy will pass those energy they have with their adjacent atoms or
molecules by means of lattice vibrations.
Image courtesy : roasterproject.com
Now we can think
how this conduction occurs in gases and liquids. In the cases of gases, the
molecules having energy in the form of kinetic energy and during their random
movements, they exchange their momentum and energy by colliding with others. By
doing so, the first molecule loses the energy while the second one gains it. This
is how energy is transferred in the case of gases.
In the case of liquids also, the working is similar to that of
gases. Here, the only difference is that, the molecules in liquids are more
closely packed and hence inter molecular forces came into action in the case of
liquids.
Fourier Law of Conduction:
Q = -kAdT/dx
Where: Q is the
heat flow rate by conduction
K is the thermal
conductivity of the material
A is the cross
sectional area normal to direction of heat flow and
dT/dx is the temperature
gradient of the section.
CONVECTION:
Conductive heat
transfer occurs within a fluid itself and it is carried out by transfer of one
fraction of the fluid to the remaining portion. Hence unlike conduction,
transfer of molecules occurs during convection. Since movement of particles
constitutes convection, it is the macro form of heat transfer. Also convection
is only [possible in fluids where the particles can moved easily and the rate
of convective heat transfer depends on the rate of flow to a great extend. Convection can be of two types:
1. Natural convection: In this
type of convection, the movement of particles which constitutes convection
occurs by the variation in densities of the fluids. As we already know, as
temperature increases, the density decreases and this variation in density will
force the fluid to move through the volume. This cause convection to occur.
2. Forced Convection: The
difference between natural convection and forced convection is that in forced
convection, a work is done to make movement in the fluid. This is done using a
pump or blower.
Newton’s Low Of Cooling:
Q = hA(Ts-T∞)
Where: Ts is the surface temperature
T∞ is the
fluid temperature
h is the heat transfer
coefficient
RADIATION
Radiation is the
third mode of heat transfer. This mode of heat transfer didn’t require any
medium to occur. Every matter having a temperature above absolute zero will
emit energy in the form of electromagnetic waves and called radiation. It is
the same way the energy of the Sun reach us. The key features about radiation
are it do not require any medium and also laws of reflection is applicable for
radiation.
Stefan- Boltzman Law:
Q = A∑Ts⁴
Where: Ts is the absolute temperature of
surface
∑ is the
proportionality constant.