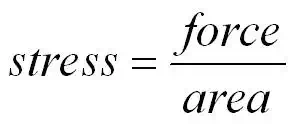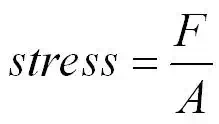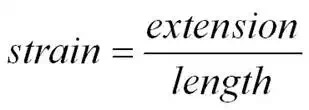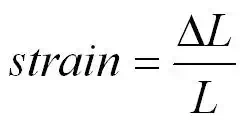Stress & Strain
Stress
The stress applied to a material
is the force per unit area applied to the material. The maximum stress a
material can stand before it breaks is called the breaking stress orultimate tensile stress.
Tensile
means the material is under tension. The forces acting on it are trying to
stretch the material. Compression is when the forces acting on an object are
trying to squash it.
The
equation below is used to calculate the stress.
stress =
stress measured in Nm-2 or
pascals (Pa)
F = force in newtons (N)
A = cross-sectional area in m2
Strain
The
ratio of extension to original length is called strain it has no units as it is
a ratio of two lengths measured in metres.
strain =
strain it has no units
DL =extension measured in metres
L = original length measured in metres
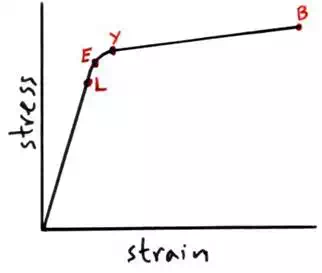
Stress-Strain graph for a ductile material
(like copper)
§ L = the limit of proportionality, Hooke’s law applies up to this point.
§ E = elastic limit, beyond this point the material is permanently stretch and it
will not go back to its original length. Elastic behaviour is when a material returns to its original length, plastic behaviour is when the stretched
material does not return to its original length.
§ Y = yield point, beyond this point small increases in force give much big
increases in length.
§ B = breaking point / breaking stress, the material breaks at this point.