Variables
After reviewing the main data types in C# let’s see how we can use them. In order to work with data we should use variables. We have already seen their usage in the examples, but now let’s look at them in more detail.
A variable is a container of information, which can change its value. It provides means for:
· storing information;
· retrieving the stored information;
· modifying the stored information.
In C# programming, you will use variables to store and process information all the time.
Characteristics of Variables
Variables are characterized by:
· name (identifier), for example age;
· type (of the information preserved in them), for example int;
· value (stored information), for example 25.
A variable is a named area of memory, which stores a value from a particular data type, and that area of memory is accessible in the program by its name. Variables can be stored directly in the operational memory of the program (in the stack) or in the dynamic memory in which larger objects are stored (such as character strings and arrays).
Primitive data types (numbers, char, bool) are called value types because they store their value directly in the program stack.
Reference data types (such as strings, objects and arrays) are an address, pointing to the dynamic memory where their value is stored. They can be dynamically allocated and released i.e. their size is not fixed in advance contrary to the case of value types.
More information about the value and reference data types is provided in the section "Value and Reference Types".
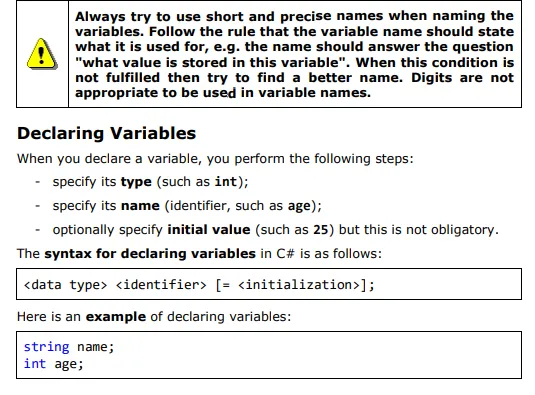
Naming Variables – Rules
When we want the compiler to allocate a memory area for some information which is used in our program we must provide a name for it. It works like an identifier and allows referring to the relevant memory area.
The name of the variable can be any of our choice but must follow certain rules defined in the C# language specification:
· Variable names can contain the letters a-z, A-Z, the digits 0-9 as well as the character '_'.
· Variable names cannot start with a digit.
· Variable names cannot coincide with a keyword of the C# language. For example, base, char, default, int, object, this, null and many others cannot be used as variable names.
A list of the C# keywords can be found in the section "Keywords" in chapter "Introduction to Programming". If we want to name a variable like a keyword, we can add a prefix to the name – "@". For example, @char and @null are valid variable names while char and null are invalid.



Variables should have names, which briefly explain their purpose. When a variable is named with an inappropriate name, it makes the program very difficult to read and modify later (after a while, when we have forgotten how it works). For further explanation on the proper naming of variables refer to chapter "High-Quality Programming Code".