Real Floating-Point Types
Real types in C# are the real numbers we know from mathematics. They are represented by a floating-point according to the standard IEEE 754 and are float and double. Let’s consider in details these two data types and understand what their similarities and differences are.
Real Type Float
The first type we will consider is the 32-bit real floating-point type float. It is also known as a single precision real number. Its default value is 0.0f or 0.0F (both are equivalent). The character 'f' when put at the end explicitly indicates that the number is of type float (because by default all real numbers are considered double). More about this special suffix we can read bellow in the "Real Literals" section. The considered type has accuracy up to seven decimal places (the others are lost). For instance, if the number 0.123456789 is stored as type float it will be rounded to 0.1234568. The range of values, which can be included in a float type (rounded with accuracy of 7 significant decimal digits), range from ±1.5 × 10-45 to ±3.4 × 1038 .
Special Values of the Real Types
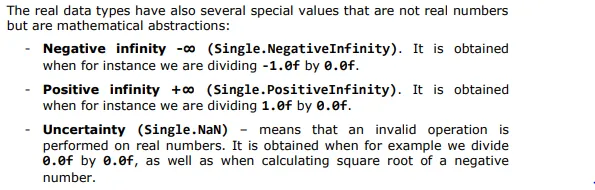
Real Type Double
The second real floating-point type in the C# language is the double type. It is also called double precision real number and is a 64-bit type with a default value of 0.0d and 0.0D (the suffix 'd' is not mandatory because by default all real numbers in C# are of type double). This type has precision of 15 to 16 decimal digits. The range of values, which can be recorded in double (rounded with precision of 15-16 significant decimal digits), is from ±5.0 × 10-324 to ±1.7 × 10308 .
The smallest real value of type double is the constant Double.MinValue = -1.79769e+308 and the largest is Double.MaxValue = 1.79769e+308. The closest to 0 positive number of type double is Double.Epsilon = 4.94066e324. As with the type float the variables of type double can take the special values: Double.PositiveInfinity (+∞), Double.NegativeInfinity (-∞) and Double.NaN (invalid number).
Real Floating-Point Types – Example
Here is an example in which we declare variables of real number types, assign values to them and print them .




