DC machines
Introduction Direct current (dc) machines were the first electrical machines that came to industrial use. The use of dc machines is now very much limited since the power supply is usually available in AC only. However, they are still used in certain applications like traction, cranes etc.
There are two types of dc machines, the dc generator and the dc motor. The dc machine which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy is called a dc generator. The dc machine which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy is called a dc motor.

Principle of dc Generator
A dc generator is a rotating machine which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. DC generators work on the principle of electromagnetic induction. According to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, whenever a conductor cuts magnetic lines of flux a dynamic emf is induced in the conductor. This emf causes a current flow if the circuit is closed. The essential requirements of a dc generator are
1. A magnetic field
2. Conductors or coils
3. Relative motion between the magnetic field and the conductors
Simple loop generator

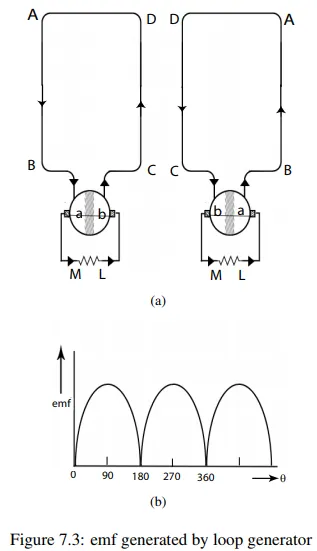
Figure 7.2 shows the arrangement of a single turn coil ABCD rotating at a constant speed in a uniform magnetic field produced by two poles. The two ends of the coil are connected to a split ring1 . An emf is induced in the coil which is proportional to the rate of flux linkage. Figure 7.3(a) shows the schematic diagram of coil connections with split ring. The direction of induced current in the coil is from A to B and from C to D during the first half revolution. Therefore the current will flow through the load resistor from M to L. In the next half revolution, the direction of induced current will be from D to C and from B to A as shown in the figure. The current will again flow from M to L through the load resistor.
In a dc generator the emf induced in the coil is alternating. In order to get a unidirectional current an arrangement known as commutator is used. The function of commutator in a dc generator is to convert the alternating current produced in the armature (coil) into direct current in the external circuit. In the figure the ends of the armature are connected to a split ring which acts as commutator.