Sectionalized Bus
An extension of the single bus configuration is the sectionalized bus arrangement shown in Figure 3. This arrangement is basically two or more single bus schemes, each tied together with bus sectionalizing breakers.
The sectionalizing breakers may be operated normally open or closed, depending on system requirements. In this arrangement, a bus fault or breaker failure causes only the affected bus section to be removed from service and thus eliminates total substation shutdown.
Usually, the fault can be isolated and non-faulted portions of the system restored to service easier and faster because of the increased flexibility of this arrangement.
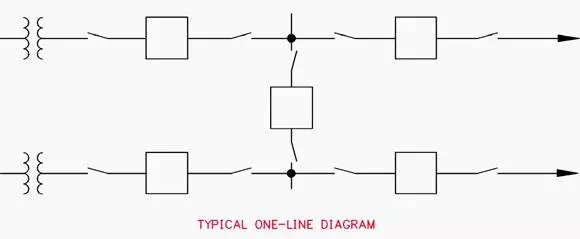 Figure 3 – Sectionalized Bus Scheme
Figure 3 – Sectionalized Bus Scheme
Physically, the equipment can be organized similar to that shown in Figures 1 and 2 for the single bus arrangement.
The sectionalizing breakers and their associated isolation switches are located in line with the main bus. In the high-profile configuration, it is usually desirable to provide a separate bay for the sectionalizing breakers and switches to facilitate maintenance and removal.
The arrangement of lines and transformers in a sectionalized bus arrangement depends on system operating criteria. They should be arranged so as to prevent outage of lines or other circuits dependent on each other.
This can be accomplished by positioning the interrelated circuits on different bus sections to eliminate concurrent shutdown. Perform a thorough analysis of all possible operational contingencies identifying any undesirable conditions preceding the final determination of circuit grouping.
Bypassing arrangements for the sectionalized bus configuration can be provided as explained for the single bus scheme.
Advantages
· Flexible operation.
· Higher reliability than single bus scheme.
· Isolation of bus sections for maintenance.
· Loss of only part of the substation for a breaker failure or a bus fault.
Disadvantages
· A sectionalized bus arrangement has a higher cost than a single bus scheme.
· Additional circuit breakers are required for sectionalizing.
· Sectionalizing may cause interruption of non-faulted circuits.