Capacitive Reactance
When the Resistor is connected in series with the capacitor forms RC circuit. In RC circuit the capacitor will charge from the D.C supply voltage and when supply voltage is decreased, eventually the capacitor also discharges by reducing its storage charge. Not only at the time of the D.C supply even in the case of A.C supply also according to the supply voltage level the capacitor will charge and discharge continually.
But due to internal resistance there will be some attenuation in the flow of the current through the capacitor. This internal resistance is called as Capacitive Reactance. ‘X_C’Indicates the Capacitive Reactance and it is measured in Ohms same as that of the resistance.
When the frequency is varied in the capacitive circuit according to the amount of frequency change this capacitive reactance value also changes. The electrons flow from one plate to the other plate causes the current flow in the circuit. But due to the movement of electrons the frequency level varies. When the frequency through the capacitor increases the capacitive reactance value decreases and when frequency through the capacitor decreases the capacitive reactance value increases. Thus, by this we can say that the capacitive reactance is inversely proportional to the applied frequency level. This shows that the capacitor connected in the circuit is dependent on supply frequency. This phenomenon is called complex impedance.
Capacitive Reactance Formula

Capacitive reactance Example

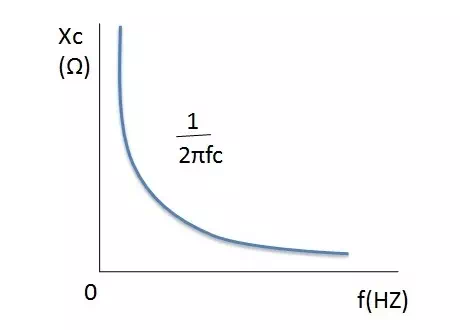
Capacitive Reactance Vs Frequency
From the above frequency verses capacitive reactance plot we can observe that when the frequency is zero the reactance value reaches to infinity this shows the phenomenon of the open circuit. When the value of the frequency increases exponentially the reactance value decreases. When frequency reaches to infinity the reactance value at nearly zero this gives us closed circuit behaviour.