What is Resistor?
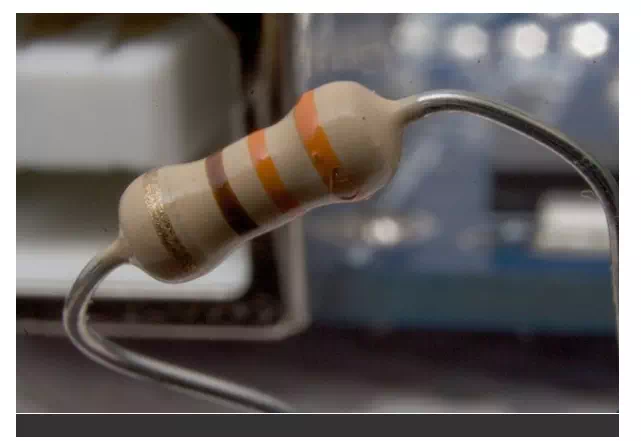
Resistor is basic component that is used in all the electronic circuits. It is a passive element that resists the flow of electrons. Thus it allows only certain amount of current to pass through it. Remaining current is converted into heat.
The working principle of bulb is that electricity is passed through the filament usually tungsten, which is a resistor. The energy is converted to and released as light and heat.

Resistor Symbols
Generally there are two standards that are used to denote the symbol of a resistor viz.Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and International Electro Technical Commissions
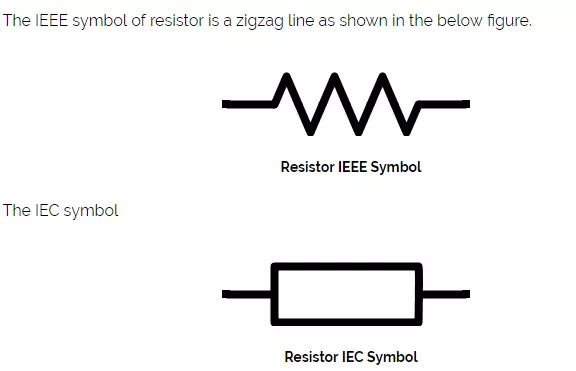
The IEEE symbol of resistor is a zigzag line as shown in the below figure.
Why is a resistor used in a circuit?
Let us take an example to answer this question.
· Consider an LED connected to a battery of 9V. Assume the Forward current of the LED is 3mA.
· If a resistor is connected between the Led and battery the Led will glow.
· If there is no resistor in between LED and battery , Led will glow but after some time it heats up enormously. This is because of the more current(>30 mA) Passing through the LED.
· Thus Resistor is necessary to control the current flow.
· Resistor used in the circuit can be used for many purposes. For example to adjust the voltage levels, to provide biasing to active components, for dividing the voltage levels etc.
Why is a resistor used in a circuit?
Consider an LED connected to a battery of 9V. Assume the Forward current of the LED is 3mA.
If a resistor is connected between the Led and battery the Led will glow.
If there is no resistor in between LED and battery , Led will glow but after some time it heats up enormously. This is because of the more current(>30 mA) Passing through the LED.
Thus Resistor is necessary to control the current flow.
Resistor used in the circuit can be used for many purposes. For example to adjust the voltage levels, to provide biasing to active components, for dividing the voltage levels etc.