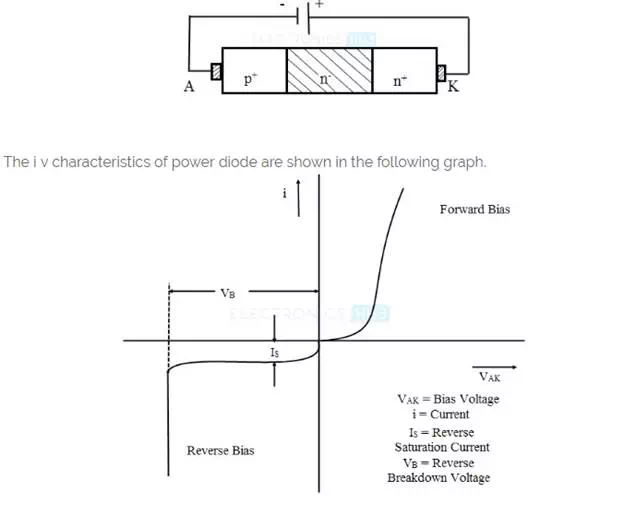
Power diode in reverse bias
Like a normal diode, a power diode also doesn’t conduct when reverse biased. Only a small amount of reverse leakage current flows in the reverse direction. For a power diode that is rated with 1000 A of forward current, only 100 m A of reverse current flows. At breakdown voltage, the reverse current increases rapidly due to impact ionization and avalanche multiplication.
Power diodes are primarily manufactured with Silicon but Gallium arsenide is also used sometimes. Materials such as Phosphorus, Arsenic and Germanium are used as dopants to form the anode (n+) while Boron, Aluminium and Gallium are used as dopants to form the cathode (p+).
Power diodes are designed to offer uncontrolled power rectification and can be used in the applications like charging of the battery, DC power supply and high voltage direct current power transmission systems as well as in rectifiers of AC circuits and in inverters. Because of their high current and high voltage characteristics they are also used as fly wheeling diodes and in waveform snubbing networks. As the power diode has a very large P-N junction area, it may not be suitable for high frequency applications i.e. for frequencies greater than 1 Mega Hertz; however design of high frequency and large current diodes is desired. Schottky Diodes are typically used for the application like high frequency rectification. The reason being their low reverse recovery time and voltage drop when forward biased.
If a single power diode is used in converting AC to DC, then it produces a half-wave varying DC. If more than one diode is used in a circuit, it produces a full-wave varying DC as it converts both positive and negative halfs of a varying AC wave into varying DC, therefore producing full-wave rectification of current. A Bridge rectifier is a type of full-wave varying DC circuit, where four diodes are connected. It provides a similar polarity output for either of the input polarities. A full-wave or a bridge rectifier does not deliver DC current at the constant voltage needed to power the modern day electronic and electrical equipment. As a result, a smoothing capacitor is usually connected at the output of the rectifier in order to smooth out the rippled voltage produced.
Power diodes use different types of IC packages. Typical examples may include the following
· DO – Diode outline
· SOD – Small outline diode
· TO – Transistor outline
· SOT – Small outline transistor
· Metal electrode leadless face.
D2PAK – Discrete package is a huge surface mounted package which
also includes a heat sink in it.
The data sheet of a power diode includes the following.
1. Forward Average current
2. Forward RMS current
3. Average Forward Power loss
While designing rectifiers using power diodes, we should never exceed these parameters.
Structurally, rectifiers can take a multiple forms, which include olden day’s vacuum tube diodes, copper and other metal oxide rectifiers and mercury arc valves. With the introduction of semiconductor electronics in recent days, rectifiers are mostly constructed from semiconductor diodes, thyristors or silicon controlled rectifiers (SCRs) (a type of thyrister) and other silicon based semiconductor switches. The process of Rectification may also serve as a source of power besides generating the direct current. As a point of note, the detectors of radio signals also serve as rectifiers. Because of the flashing and varying nature of the AC sine wave, the rectification process alone itself produces a DC current which is unidirectional also consists of pulses of current. Many applications of rectifiers include power supplies for radio, television, computer and other electronic communication equipment which require a stable and constant DC current. In these electronic applications, the output of the rectifier is smoothed by an electronic smoothing filter or a capacitor to produce a constant form of current.
In the rectification from very low to high currents, various kinds of semiconductor diodes such as junction diodes and Schottky diodes, etc., are broadly used. Various types of silicon based semiconductor devices are used in high power rectifiers, such as those used in higher voltage direct current power transmission systems. The silicon based semiconductor devices include thyristors and many other controlled solid state switches effectively function as diodes to pass direct current solely in one direction.
Rectifier circuits can be classified as either single phase or multi phase based on the type of the alternating current. Most of the low to medium power rectifiers for household equipment are single phase whereas three phase rectifiers are very crucial for industrial applications and also in the process of transmission of energy as DC.
A variety of rectifier circuits are available today. They may be Half Wave, Full Wave and/or Bridge Rectifiers. Each type of these rectifier circuits can be categorized as either uncontrolled, a half-controlled or a fully controlled device.