Anti-Logarithmic Amplifier or Exponential Amplifier
Anti-logarithmic or exponential amplifier (or simply antilog amplifier) is an op-amp circuit configuration, whose output is proportional to the exponential value or anti-log value of the input. Antilog amplifier does the exact opposite of a log amplifier. Antilog amplifiers along with log amplifiers are used to perform analogue computations on the input signals. The circuit of an antilog amplifier using op-amp is shown in the figure below.
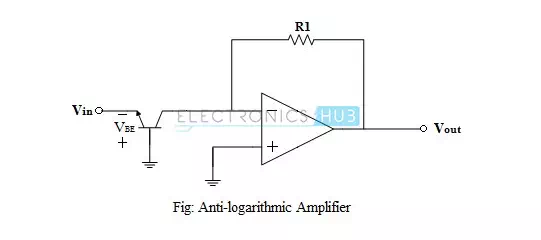
It is noted that by exchanging the positions of the transistor and the resistor, the log amplifier can be made to work as antilog amplifier. The base-collector voltage of the transistor is maintained at ground potential, from the virtual ground concept. The current IE for the transistor is given by,
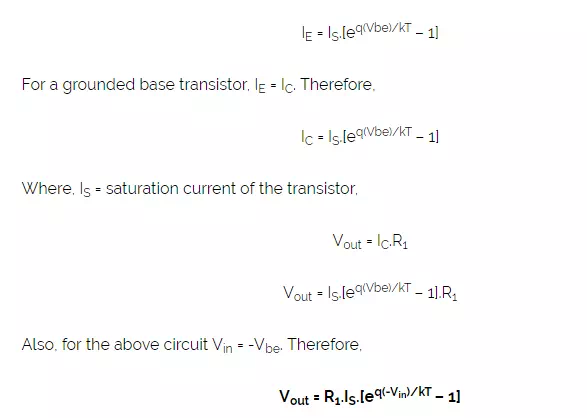
Antilog amplifiers also suffer from unstable outputs, due to the variations in IS for different transistors and temperature dependence. Compensating circuits can be added to stabilize the output against such variations.