How do Solid State Drives Work?
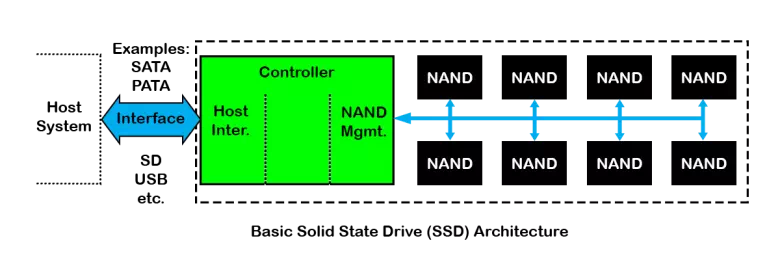
A Solid State Drive emulates a hard disk drive in a host computer or embedded system. It does this with a specially designed controller which has the same electrical interface as a rotating hard disk drive. In many cases it has the exact same connector and physical form factor as the hard drive as well.
Other circuitry of the controller manages the NAND flash memory which stores the data of the SSD. While the controller function appears relatively straight forward, there are many behind the scenes issues with NAND flash management and it requires a great deal of planning to create a reliable SSD controller.
How long do Solid State Drives last?
The life of a SSD depends on the application which it is being used. Unlike rotating hard disk drives which SSD were designed to replace, the SSD memory has a finite number of endurance/erase cycles. This makes the management of data written to the SSD extremely important. As an example, a consumer 2.5” SATA SSD could last for decades in low intensity application, but may only last a few weeks in a high intensity data logging application.
There are also different types of NAND flash memory which range from the highest reliability and cost Single Level Cell (SLC) to the lowest cost and reliability Tri Level Cell NAND. It is important when choosing a SSD to select the one which is right for the application.
Solid State Drive vs Hard Drive

As the SSD has proliferated in the market, “What are the differences of Solid State Drive vs Hard Drive,” is a common question.
A Solid State Drive has no moving parts compared to a hard disk drive which has a two major moving components –
1. A spindle motor to rotate one or more layers of platters
2. An actuator to move a read/write “head” across the platters
A solid state drive is made of all semiconductor components, so shock & vibration resistance is significantly better than the hard disk drive. Other superior attributes of SSD are lower power usage and better performance – especially small blocks of data.
Hard disk drives are still in the market because they can deliver higher capacities at a lower price point than SSD.