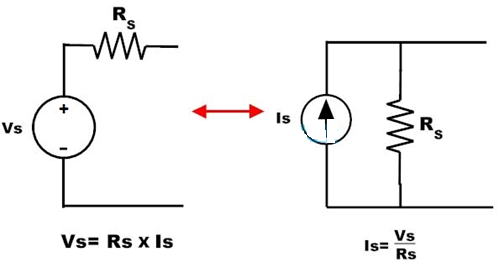
Conversion of Voltage Source to Current Source
From the above discussion a voltage source can be converted or transformed into a current source by interchanging a series resistor to parallel as shown in figure.

Steps:
· Find the internal resistance of the voltage source and keep this resistor in parallel with a current source.
· Determine the current flow provided by current source by applying ohms law.
In the above figure, a voltage source with a resistance Rs is transformed into an equivalent current source with a parallel resistor Rs. And this current value is obtained by applying the simple ohms law as
Is = Vs/Rs.
Example:
Consider the below voltage source circuit with a voltage of 20 V and a internal resistance of 5 ohms. This circuit is transformed into the current source by placing a resistor of the same value with a current source. This current source value can be determined by,
Is = Vs/Rs
= 20/ 5
= 4 amps
The equivalent current source with a current of 4A and parallel resistor of 5 ohms is shown below.
Conversion of Current Source to Voltage Source
The current source transformed into a voltage source by interchanging parallel resistor in series. Let us see how it could work.
Steps:
· Find the parallel resistance of the constant current source and place in series with a voltage source.
· Determine the open circuit voltage value of the voltage source by applying ohms law.
In the above figure, a current source is converted into a voltage source by placing resistance Rs in series with a voltage source and the value of the voltage source is calculated as,
Vs = Is *Rs
Example:
Consider the below example for current source transformation, where current source is of 10A with a parallel resistance of 3 ohms. To calculate the value of voltage in voltage source apply the simple ohms law, then,
Vs = Is * Rs
Vs = 10 * 3
= 30 Volts.
Therefore the equivalent voltage source of this transformation consists a voltage source 30 V with a series resistance 3 ohms.