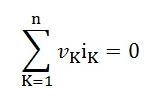
Tellegen’s Theorem
Tellegen’s Theorem states that the summation of power delivered is zero for each branch of any electrical network at any instant of time. It is mainly applicable for designing the filters in signal processing. It is also used in complex operating systems for regulating stability. It is mostly used in the chemical and biological system and for finding the dynamic behaviour of the physical network.
Tellegen’s Theorem can also be stated in another word as, in any linear, nonlinear, passive, active, time-variant or time-invariant network the summation of power (instantaneous or complex power of sources) is zero.
Thus, for the Kth branch, this theorem states that:
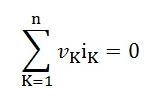
Where,
n is the number of branches
vK is the voltage in the branch
iK is the current flowing through the branch.
Let,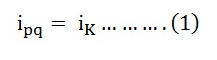
Equation (1) shows the Kth branch through current
vK is the voltage drop in branch K and is given as:
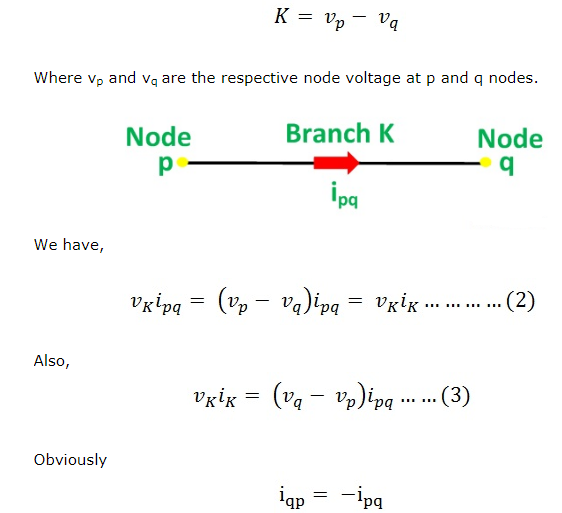
Summing the above two equations (2) and (3), we get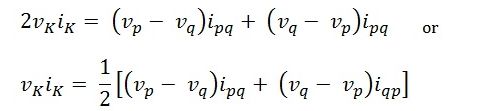
Such equations can be written for every branch of the network.
Assuming n branches, the equation will be: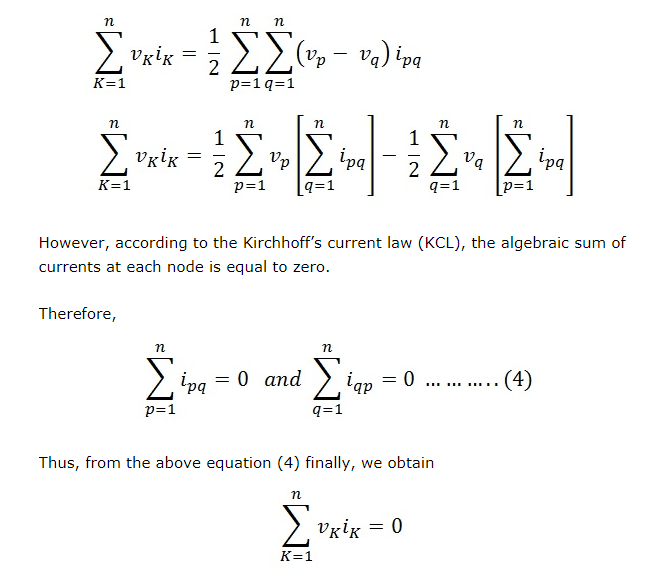
Thus, it has been observed that the sum of power delivered to a closed network is zero. This proves the Tellegen’s theorem and also proves the conservation of power in any electrical network.
It is also evident that the sum of power delivered to the network by an independent source is equal to the sum of power absorbed by all passive elements of the network.
The following steps are given below to solve any electrical network by Tellegen’s theorem:
· Step 1 – In order to justify this theorem in an electrical network, the first step is to find the branch voltage drops.
· Step 2 – Find the corresponding branch currents using conventional analysis methods.
· Step 3 – Tellegen’s theorem can then be justified by summing the products of all branch voltages and currents.
For example, if a network having some branches “b” then:
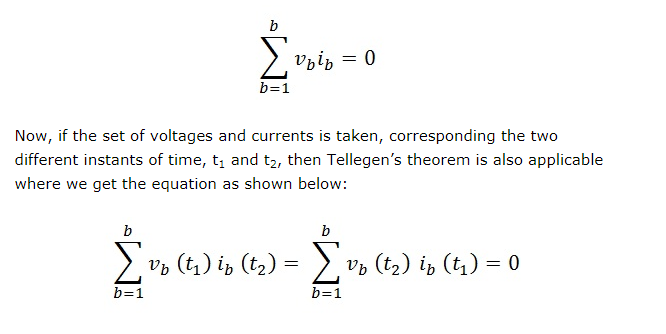
The various applications of the Tellegen’s theorem are as follows:
· It is used in the digital signal processing system for designing filters.
· In the area of the biological and chemical process.
· In topology and structure of reaction network analysis.
· The theorem is used in chemical plants and oil industries to determine the stability of any complex systems.