Inductors
Let me introduce you to another important component in the field of Electronics and Electricals, the Inductor. Inductor is a passive two-terminal component that temporarily stores energy in the form of a magnetic field. It is usually called as a coil. The main property of an inductor is that it opposes any change in current.
Inductor
According to the Faraday’s law of Electromagnetic induction, When the current flowing through an inductor changes, the time-varying magnetic field induces a voltage in the conductor. According to lens law, the direction of induced EMF opposes the change in current that created it. Hence, induced EMF is opposite to the voltage applied across the coil. This is the property of an inductor.
The following figure shows how an inductor looks like.

An inductor blocks any AC component present in a DC signal. The inductor is sometimes wrapped upon a core, for example a ferrite core. It then looks as in the figure below.
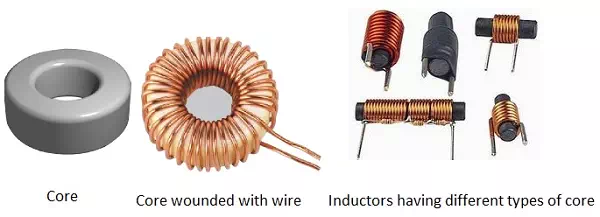
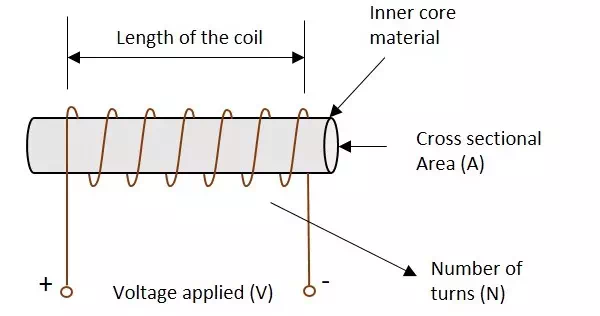
The following figure shows an inductor with various parts labelled.
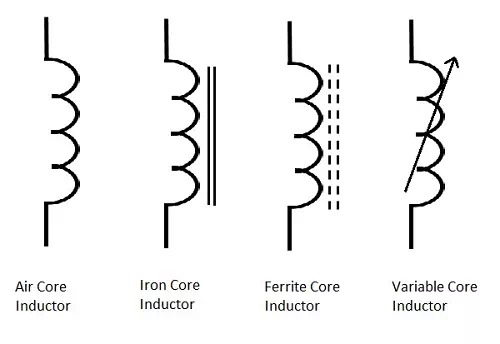
Symbols
The symbols of various types of inductors are as given below.
Storage of Energy
One of the Basic properties of electromagnetism is that the current when flows through an inductor, a magnetic field gets created perpendicular to the current flow. This keeps on building up. It gets stabilized at some point, which means that the inductance won’t build up after that. When the current stops flowing, the magnetic field gets decreased.
This magnetic energy gets turned into electrical energy. Hence energy gets stored in this temporarily in the form of magnetic field.