Thin Film
Thin film resistors have a resistive layer of width 0.1 micrometer or smaller on the ceramic base. Thin film resistors have a metallic film that is vacuum deposited on an insulating substrate.
Thin film resistors are more accurate and have better temperature coefficient and is more stable. The thin film resistors are further divided into two types such as −
- Carbon film resistors
- Metal film resistors
Carbon film resistor
A Carbon film resistor is made by depositing a carbon film layer on a ceramic substrate. The carbon film acts as the resistive material to the current and the ceramic substance acts as an insulating substance. Metallic caps are fixed at both the ends and copper leads are drawn out.
The following figure shows the construction of a carbon film resistor.
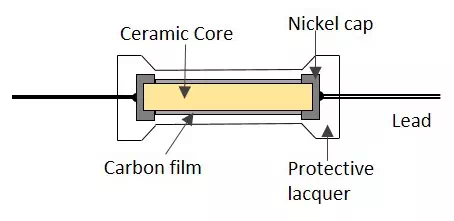
The main advantages of these resistors are their high stability, wide operating range, low noise, and low cost. The carbon film resistors are the most preferred ones over carbon composition resistors due to their low noise.
Metal Film Resistors
The film coating makes the difference between metal oxide film resistors and metal film resistors. A thin film of metallic substance such as nickel chromium is used to coat the resistor in a metal film resistor whereas a film of metal oxide like tin oxide is used to coat the resistor in a metal oxide resistor.
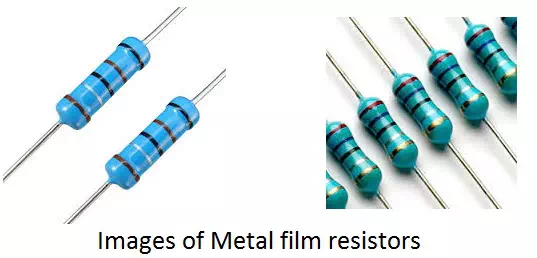
Metal film resistors have low temperature coefficient of resistance, which means the resistance is less affected by the temperature.