Thick Film
The film resistors have a resistive layer on a ceramic base, whose thickness defines the type they belong to. The thickness of resistive layer on thick film resistors is much higher than thin film resistors. Thick film resistors are produced by firing a special paste, which is a mixture of glass and metal oxides, onto the substrate.
There are three main types in thick film resistors like Fusible resistors, Cermet film resistors, and Metal oxide film resistors.
Fusible Resistors
The Fusible resistors are similar to wire wound resistors. But these resistors along with providing resistance, act as a fuse. The image of a fusible resistor is as shown below.

In this resistor, the current flows through a spring loaded connection, which is placed closely to the body of the resistor. The blob that is attached to the spring wire of the resistor takes the heat generated by the resistor due to the current flow. If this heat is increased, the attachment to the blob gets melted up and opens the connection.
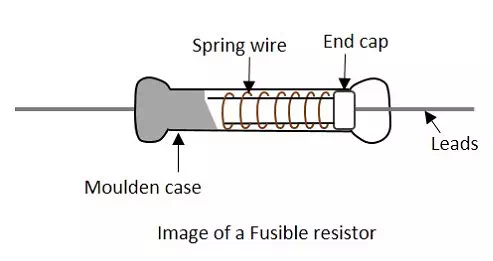
Hence we can say that, these resistors limit the current, but if the circuit power rating exceeds a specified value, these resistors act as a fuse to open or break the circuit. The value of these resistors is usually of less than 10 Ohms. These resistors are generally used in TV sets, amplifiers and other expensive electronic circuits.
Cermet Film Resistors
The Cermet film resistors are the film resistors made up of a special material called Cermet. Cermet is a composite alloy made by combining Ceramic and Metal. This combination provides the advantages in both of these materials like high temperature resistance and wear resistance of ceramic along with flexibility and electrical conductivity of a metal.

A metal film layer is wrapped around a resistive material and is fixed in a ceramic metal or cermet substrate. Leads are taken to make the connections easy while fixing on a PCB. They offer high stability as temperature cannot affect their performance.
Metal Oxide film resistors
A Metal oxide film resistor is formed by oxidizing a thick film of Tin chloride on a heated glass rod, which is a substrate. They have high temperature stability and can be used at high voltages. These resistors have low operating noise.

Metal oxide film resistors differ with metal film ones only regarding the type of film coated. Metal oxide is a metallic compound like tin with oxygen to form tin oxide, which is coated as a film on the resistor. The resistivity of this resistor depends upon the amount of antimony oxide added to the tin oxide.