Dc load line
What is DC Load
Line Analysis and Its Significance
In 1835 the Lloyd’s Register Group Limited introduced loading
recommendations. The load line-markings are invented by Samuel Plimsoll (10 February
1824-3rd June 1898) in 1876. The main intention of the load line is to find
the overloaded ships using the load line markers on the ship and
these are found on side of the ship. In this article, we get to know the
purpose of load lines and how they are used to find the loaded ships using the
markers. So, this article discusses an overview of the dc load line analysis
and its markings.
What is DC
Load Line Analysis?
Definition: The DC
(Direct Current) load line is a graph that has all possible volumes of output
current (Ic) and output
voltage (VCE) for a given amplifier. In the case of the amplifier, it
has two inputs they are AC input and DC input. If we analyze
the circuit for DC input then it is called a DC analysis. Similarly, if we have
only AC input while analyzing then it is called AC
analysis. If there are multiple sources available in the circuit you can treat
one source at a time by using the superposition theorem.
Transistor
DC Load Line
The transistor consists of the collector, emitter, and bias. The circuit
diagram of the dc load line using a transistor is shown below. As shown in the
figure, the DC battery VBB is applied at the base and
the collector terminals of the transistor. The voltage between collector and
emitter is called VCE and voltage between bias and
emitter is called VBE. To get the dc load line, we need to apply
Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law to the output.
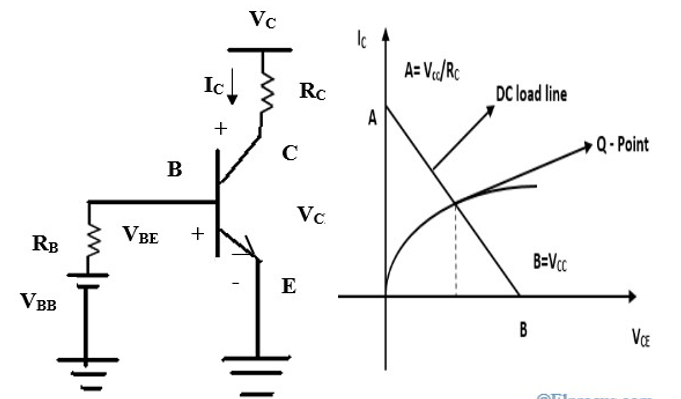
transistor-dc-load-line
By
applying Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law to output will get
VCC-IC*RC-VCE = 0
Hence we
can write the above equation as
IC*RC = -VCE +VCC
Hence IC = -1/ RC * VCE +
VCC
To draw
the dc load line, we require a minimum of two points they are
Case 1: If we put IC =
0, then will get VCE = VCC
Case 2: If we put VCE =
0, then IC becomes VCC / RC
By using the above two cases we can easily draw the dc load line for
output characteristics. The dc load line is a graph of all values of IC and
VCE. For common emitter configuration, the IC and
VCE will be on output characteristics that’s why dc load line
is drawn at output characteristics. If we plot using the above two cases, we
will get the slope line and that line is called the dc load line.
The operating point ‘Q’ is defined as a point for a particular value of
IC and the corresponding value of VCE. We have to select the Q point
exactly in the middle of the load line. When output characteristics intersect
dc load line we can get different Q points.
Load Line
Markings on Ships Side
A cargo
ship is designed to carry different weights and volumes of cargo under the safe
limit to avoid grounding and sinking of the vessel. The load line markers on a
ship are shown in the below figure.
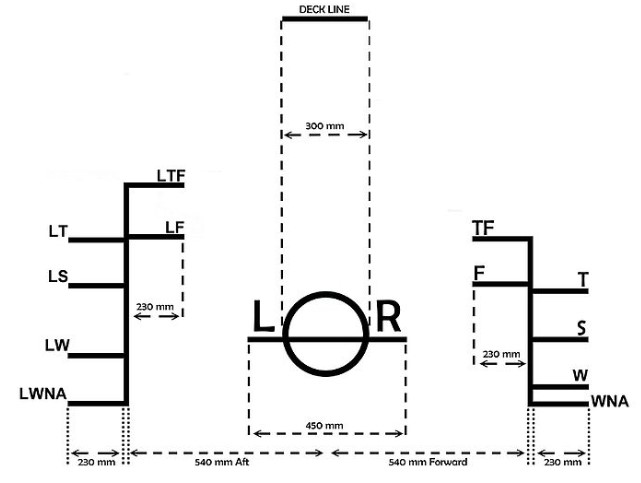
Load-line-markers
As shown
in the above figure, the horizontal line is the deck line with a diameter 300mm
and the round shape disc is the load line disc. From the center
of the disc, the vertical lines are placed at a distance of 540mm. There are
two types of load line markings they are standard load line-markings and timber
load line-markings.
Standard
Load Line Markings
The upper
surfaces of the load line indicate the maximum depths to which the ships may be
submerged in different seasons and circumstances. The letter ‘S’ in the load
line marker is the Summer load line, it is the basic freeboard line at the same
level as the plimsol line and other load lines are
marked based on the summer freeboard line.
The letter
‘T’ in the load line marker is a tropical load line,
it is 1/48th of the summer draft marked above the summer load line. The letter
‘W’ in load line marker is winter load, it is also a
1/48th of the summer draft marked below the summer load. The letter ‘WNA’ in
the load line marker is winter North Atlantic load line is marked 50mm below
the winter load line, it applies voyages in North
Atlantic (above 36 degrees of latitude) during winter months.
The
freshwater load line represented by a letter ‘F’, it is the summer fresh water
line, the distance between summer and the freshwater line is the freshwater
allowance. The Tropical freshwater load line is the freshwater load line in
tropical and it is represented by TF, it is marked above the tropical line at
an amount equal to freshwater allowance (FWA)
Timber
Load Line Markings
The LS
(Lumber Summer), LW (Lumber Winter), LT (Lumber Tropical), LWNA (Lumber Winter
North Atlantic), LF (Lumber Fresh Water), and LTF (Lumber Fresh Water) are the
timber load line-markings.
It is
important for any ship to have a safe draft for safety and to avoid grounding.
The draft can be measured vertically between the keel and the waterline of the
ship. If the ship is loaded with more cargo, the draft will increase. The load
line also helps in determining the freeboard of the ship which is the distance
between the sheer and the waterline. Again if the draft increases, which means
more volume of the cargo has been loaded leading to the decrease in the freeboard.
If the freeboard is reduced more than the required limit, it may sink the
vessel.
DC Load
Line Analysis Significance
The significances of the DC load line are
![]() By using the direct current load line concept, we can
obtain the linear analysis of the circuit for non-linear elements such as
diodes or transistors
By using the direct current load line concept, we can
obtain the linear analysis of the circuit for non-linear elements such as
diodes or transistors
![]() The DC load line analysis main intention is to find
the Quiescent Point (Q – point)
The DC load line analysis main intention is to find
the Quiescent Point (Q – point)
![]() The Quiescent Point obtain by
the dc load line at which the parameters voltage and current are equivalent to
each other for both the parts of the circuit.
The Quiescent Point obtain by
the dc load line at which the parameters voltage and current are equivalent to
each other for both the parts of the circuit.
![]() The signals amplified in dc load lines are less than
the millivolts
The signals amplified in dc load lines are less than
the millivolts
![]() The Quiescent Point obtained is essential while
drawing the alternate current load lines
The Quiescent Point obtained is essential while
drawing the alternate current load lines
![]() The dc voltage applied to the circuit varies when the
resistance is constant
The dc voltage applied to the circuit varies when the
resistance is constant