Enhancement-mode MOSFET
The more common Enhancement-mode MOSFET or eMOSFET, is the reverse of the depletion-mode type. Here the conducting channel is lightly doped or even undoped making it non-conductive. This results in the device being normally “OFF” (non-conducting) when the gate bias voltage, VGS is equal to zero. The circuit symbol shown above for an enhancement MOS transistor uses a broken channel line to signify a normally open non-conducting channel.
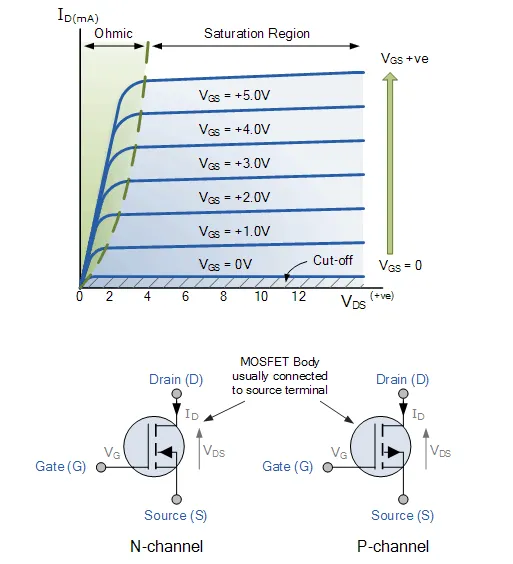
For the n-channel enhancement MOS transistor a drain current will only flow when a gate voltage ( VGS ) is applied to the gate terminal greater than the threshold voltage ( VTH ) level in which conductance takes place making it a transconductance device.
The application of a positive (+ve) gate voltage to a n-type eMOSFET attracts more electrons towards the oxide layer around the gate thereby increasing or enhancing (hence its name) the thickness of the channel allowing more current to flow. This is why this kind of transistor is called an enhancement mode device as the application of a gate voltage enhances the channel.
Increasing this positive gate voltage will cause the channel resistance to decrease further causing an increase in the drain current, ID through the channel. In other words, for an n-channel enhancement mode MOSFET: +VGS turns the transistor “ON”, while a zero or -VGSturns the transistor “OFF”. Thus the enhancement-mode MOSFET is equivalent to a “normally-open” switch.
The reverse is true for the p-channel enhancement MOS transistor. When VGS = 0 the device is “OFF” and the channel is open. The application of a negative (-ve) gate voltage to the p-type eMOSFET enhances the channels conductivity turning it “ON”. Then for an p-channel enhancement mode MOSFET: +VGS turns the transistor “OFF”, while -VGS turns the transistor “ON”.
Enhancement-mode N-Channel MOSFET and Circuit Symbols

Enhancement-mode MOSFETs make excellent electronics switches due to their low “ON” resistance and extremely high “OFF” resistance as well as their infinitely high input resistance due to their isolated gate. Enhancement-mode MOSFETs are used in integrated circuits to produce CMOS type Logic Gates and power switching circuits in the form of as PMOS (P-channel) and NMOS (N-channel) gates. CMOS actually stands for Complementary MOS meaning that the logic device has both PMOS and NMOS within its design.