Limitations of superposition Theorem
Superposition theorem doesn’t work for power calculation. Because power calculations involve either the product of voltage and current, the square of current or the square of the voltage, they are not linear operations. This statement can be explained with a simple example as given below.
Example: Consider the circuit diagram as shown in fig
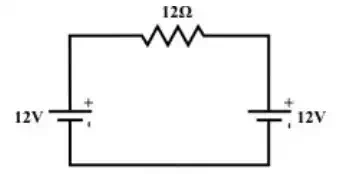
Using superposition theorem one can find the resultant current flowing through 12Ω resistor is zero and consequently power consumed by the resistor is also zero. For power consumed in an any resistive element of a network cannot be computed using superposition theorem. Note that the power consumed by each individual source is given by
![]()
The total power consumed by 12 Ω = 24 watts (applying superposition theorem). This result is wrong conceptually. In fact, we may use the superposition theorem to find a current in any branch or a voltage across any branch, from which power is then can be calculated.
· Superposition theorem cannot be applied for nonlinear circuit ( Diodes or Transistors ).
· This method has weaknesses:- In order to calculate load current LI or the load voltage for the several choices of load resistance of the resistive network , one needs to solve for every source voltage and current, perhaps several times. With the simple circuit, this is fairly easy but in a large circuit this method becomes a painful experience.
Test Your Understanding
1. When using the superposition theorem, to find the current produced independently by one voltage source, the other voltage source(s) must be ----------- and the current source(s) must be --------------.
2. Use superposition theorem to find the value of the voltage in fig
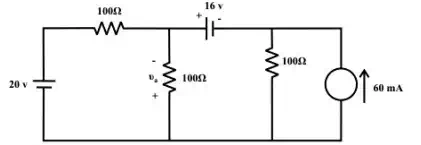
(Ans. 14volts )
3. Using superposition theorem, find the current i through 5Ω resistor as shown in fig.
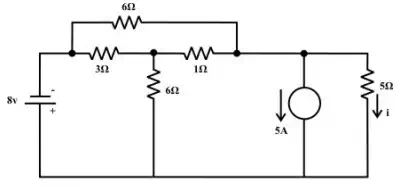
(Ans. − 0.538 A)