How Windmills Generate Electricity
How do windmills generate
electricity? The windmills are now in popular favor as
the solution of our electricity needs and for being green. We discuss the types
of windmills, the history, its construction, and working principle in this
article.
History of Wind Mills
How do windmills generate
electricity? Though Don Quixote attacked the windmill, it is no monster. It is
an important invention which can help us to reduce our carbon footprint and
save our earth from global warming. In various parts of the world and coastal
areas, there is an abundance of breeze. These windmills, if installed, can
generate large amounts of electricity to serve the needs of the local people.
Historically windmills have
been used for the grinding of the grains into flour, for taking out water from
wells, and for similar other applications. Wind energy has been used by man for
a very long time. The earliest recorded practical windmills were said to be
used in Sistan in Afghanistan around 7th to
8th century and was used for pumping water as well as grinding corn. In Europe
windmills surfaced around the twelfth century. In Denmark where the sea breeze
is abundant there were an estimated 2500 windmills around 1900. In fact Germans
used wind turbines in WW II to recharge the batteries of their U boats.
Nowadays you see windmills in
all places where breeze is abundant. In many countries they are a significant
means of power generation. On the coasts of Gujarat in India you see a large
number of windmills. Windmills have a simple working principle, need less maintenance, and last long as other means of
power generation.
Wind energy has re-emerged as
a significant source of energy in the minds of power engineers due to the
following reasons:
1. The need for new sources of energy as the
fossil fuel reserves are declining.
2. The potential is great as wind energy
exists at many places all over the world, and at some places the density is
very high, making the prospects attractive.
3. With advances in technology, the highly
efficient windmill airfoil design gives a
high efficiency and can be profitably produced.
4. The last and most important is the
political will, which was lacking until now. With the media discussing the
effects of global warming and the common man becoming aware of it, we are now
worried for the future.
Wind Mills
Types of Wind Mills
The modern windmill is more
correctly called as a wind turbine as it can generate electrical power. (The
older windmills in contrast generated mechanical power.) Wind turbines are
primarily divided into horizontal axis windmills and vertical axis windmills.
The horizontal axis wind turbines are of the following types:
5. Single bladed
6. Double bladed
7. Three bladed
8. US farm windmill multi-bladed
9. Bicycle multiple bladed
10. Upwind
11. Downwind
12. Sail wing
13. Multi-rotor
14. Counter rotating blades
15. Cross wind savonius
16. Cross wind paddles
17. Diffuser
18. Concentrator
19. Unconfined vortex
The vertical axis windmills
are of the following types:
20. Savonius
21. Multi-bladed savonius
22. Plates
23. Cupped
24. Darrieus
25. Giromill
26. Turbine
27. Magnus
28. Airfoil
29. Deflector
30. Sunlight
31. Venturi
32. Confined vortex
Working Principle of Wind Mills
A wind turbine is a machine
that coverts wind energy into electricity. The generators are connected to
battery charging circuits and finally to large utility grids. In windmills the
wind passes through the airfoil section of
the blades and the lift produced generates a torque which is then transformed
to electricity in the generator. It is basically the conversion of the wind
energy into the mechanical energy of the turbine and then finally to
electricity. As the output of the wind turbine is dependent on the availability
of the winds it is intermittent and undependable. They can however be used
along with conventional generators in a large grid and can reduce the loads of
these generators when they are generating. The other option is to use storage
devices like batteries and then discharge the electricity uniformly.
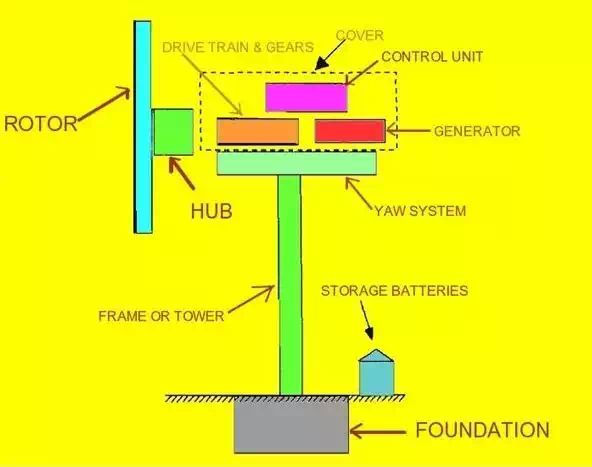
The main parts of the
windmills are as follows:
33. The rotors consisting of the blades and the hub.
34. The drive train and gears along with the mechanical brakes.
The brakes are used in the maintenance work and when a storm is coming.
35. The generator which generates electricity.
36. The yaw system which rotates the housing toward the
direction of the wind.
37. Tower and foundation.
38. Battery and the electrical system to transmit to the grid.
The working principle is that
when the wind passes through the blades, the blades experience a lift due to
the aerodynamic airfoil shape. Due to the
lift produced, the blades move and start rotating. The yaw unit aligns it
towards the incoming wind direction when the winds change. The rotation of the
blades is transmitted through the gear train and couplings to the generator
that generates electricity. The electricity is then transmitted through the
wires to the storage batteries or directly to the grid.
Construction of a Wind Mill