Journey Of Electricity: From
Power House To Your House
Learn about the basic facts of
electricity transmission and what all is required to transport power to your
homes and offices
Introduction
Electricity is perhaps one of
the greatest inventions of modern times just as fire was that of ancient times.
We are so used to using electricity and it has such a deep effect on our lives
that we literally take it for granted. Whenever we need to use electricity, we
simply throw a switch in the ON position without ever bothering that exactly
how does this magic vibration get across to us from where it is actually
generated. The journey of electricity from the power station to your home is
really an interesting and exciting one. It falls under the purview of
electrical power system studies and includes power transmission as well as
distribution, which we shall study in detail as well progress in this journey.
Electric Transmission and Distribution
Even if you donít know much
about the technicalities involved in transmission and distribution, I am sure
we have all seen huge transmission lines whenever we are cruising leisurely
across the road in your car. Just see the adjacent picture to know what I am
talking about. These towers are but a part of the entire network of equipment
and paraphernalia which are used to transport bulk electrical energy from the
power house to the final consumer point.

Basically the above process
consists of two different parts. The process of transporting the power from the
generating station to the sub-station comes under transmission, while the
process of distribution of power from the sub-station to individual consumers
comes under power distribution. Hence you can see that they are both extensions
of the same process. Do not worry if you do not fully understand the various
terms and equipments mentioned here for we
will be dealing with them in detail in our later articles.
Basic Supply System Setup
Electricity mainly comes in
two forms namely alternating current and direct current. Each of these has
their own distinct uses. We will study about the transmission and distribution
of both these types of current. Yet there are a few basic concepts which hold
true for either of them and these have been defined as follows.
○ Since power is a precious and scarce resource,
it must be ensured that the losses in the transmission and distribution system
are kept to a minimum level. Of course some losses are unavoidable since it is
not possible to have a totally loss-free transmission.
○ Since cost of power generation,
transmission and distribution are passed on to the consumers; it should be
ensured that the techniques and materials used for transmission are not overly
expensive so that electricity costs are maintained within reasonable levels.
○ Transmission lines pass through various
locations including roadsides, fields and so forth. There are human beings at
most of these places and their safety from high voltages should be ensured by
keeping the system at optimum insulation level.
○ The current in the transmission system
should be maintained within reasonable levels since heat produced is
proportional to current and it could result in overheating of the conductors
apart from increasing power loss.
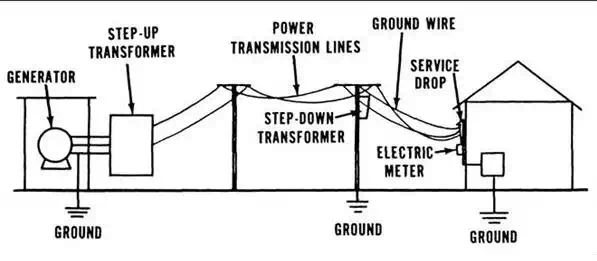
A schematic of a simple transmission/distribution
system is shown in the adjoining figure which clearly shows the various steps
involved transferring power from generation point to the point where it finally
gets consumed. The main components such as generators, transformers and grounding are
shown which will be discussed at later stages.
In our next article we will
study about overhead and underground transmission systems and other aspects of
power distribution.