Transformer construction
1. Basic construction of transformer
A basic transformer has simplest construction with primary winding set, secondary winding set and core. Core is the medium for passing the magnetic flux from primary winding to secondary winding. Generally iron core is used because it has higher permeability for magnetic flux. It means heat transfers better in iron then in wood and same as magnetic flux transfers or passes better in iron core then the air.
2. Why there is iron core instead of air core in transformer
Time-varying mutual flux
links the both primary and secondary winding in transformer. It is required
that most of the flux is to be confined to a definite, high-permeability path
linking the windings. Now with air ore it is not possible but with core of iron
or other ferromagnetic material coupling is effectively done. Because most of
the flux in iron core is confined to a definite, high-permeability path linking
the windings.
[adcc]
3. Iron core in transformer-
As the iron core is also under the flux variation in transformer there is some voltage induced in the iron core. This voltage is called the eddy voltage and in result there is a current named eddy current flow in the iron core. These results in heating up the core. With a solid iron core the eddy current is high.
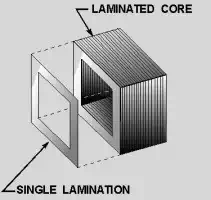
Stack of laminated core of transformer.To avoid this solid iron core is not used. Thin iron core is laminated to make it non-conductive. Then this thin laminated core is stacked by several to get the complete iron core structure. With this modification eddy current is reduced but magnetic property of the iron core is remained unchanged.
To reduce the losses caused by eddy currents in the core, the magnetic circuit usually consists of a stack of thin lamination.
4. Materials of iron core of transformer-
· Silicon steel for low cost, low core loss, and high permeability at high flux densities (1.0 to 1.5 T).
· Compressed powdered ferromagnetic alloys known as ferrites- used in the core of small transformer used in communication circuits at high frequencies and low energy levels.