Capacitor with DC & AC voltage – what are the difference.
A capacitor is in its basic version is two electrical conductor plate or body separated by some insulating medium. It stores energy in the form of electrical charge.
A capacitor can be represented by an insulating layer between two conductor plates (armatures)
Capacitor with Direct Voltage:
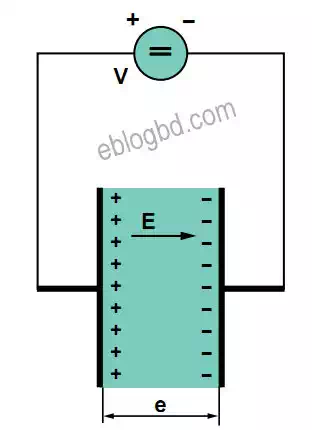
Capacitor with dc voltage
If a direct voltage is applied across the terminals the armatures are charged with a quantity Q of electricity.
Energy W is stored and an electrical field E is established in the dielectric. As soon as the capacitor is charged, the current stops flowing (except for a very small quantity of leakage current).
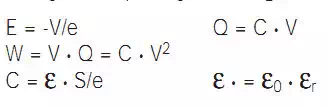
C: capacitor capacitance in Farad (F)
ε • = dielectric permittivity in F/m
εr = relative permittivity of the insulating material
ε0 = 8.85 • 10-12 F/m
Capacitor blocks current in DC voltage. Though there might be some leakage current- depends upon the voltage level & di-electric medium.
Capacitor with AC voltage
Energy is stored and restored 100 or 200 times per second depending on the network frequency. A current flows, rather than transitory it is periodic, corresponding to the capacitor charge and discharge.
v = V0 sin ωt
i = dQ/dt et Q = C • V
i = C • dV/dt = Cω V0 cos ωt
As an rms value
I = C ω V
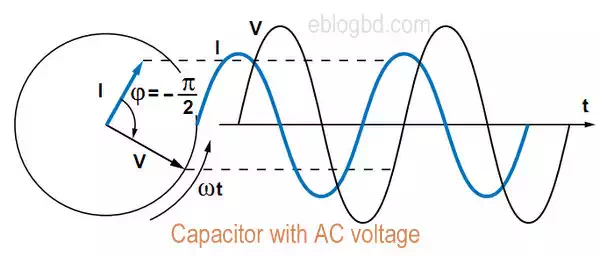
i leads v by 1/4 of a cycle
 Capacitor
with ac voltage- The voltage is lag behind the current.
Capacitor
with ac voltage- The voltage is lag behind the current.
· Capacitor let pass the current in AC voltage but with a shift of phase between voltage and current. The voltage is lag behind the current.