Load impedance effect on incident wave and reflection wave due to surge.
We know the term transmission and reflection coefficient of a medium when they are to transfer any sorts of wave due to fault, communication signal wave, micro wave signal.
Now if the lightning strike happens, the created incident wave will be created and propagate through the medium surroundings plus there will be reflected wave too. As our sole purpose to design an effective model of lightning protection, we have to understand the behaviour of different electrical system towards the incident wave.
Why Impedance has major impact of incident wave
The main parameter of electrical system that has an impact on incident, reflection wave is the Impedance of the individual electrical system. Each electrical system has own impedance, you can find it documentation from manufacturer or there is some average chart impedance list of electrical system.
High impedance loads, compared to the network’s typical impedance, must be considered as open network points (for example transformers).
At these points, the superposition of the incident wave and the reflected wave creates local dielectric stress (critical point) which can reach up to twice the wave value. In certain cases, waves that have already been contained by a surge arrester, are still capable of creating stress in an installation above the level for which it was foreseen.
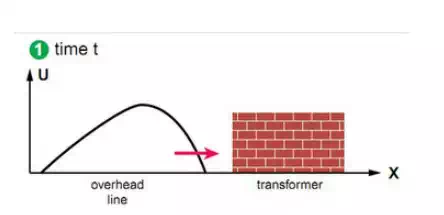
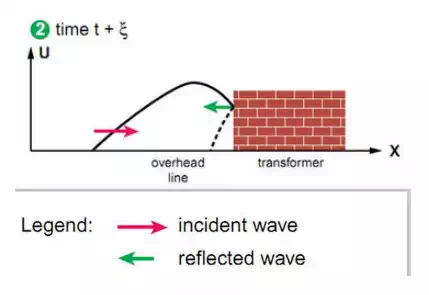
High impedance creates reflected wave of incident wave
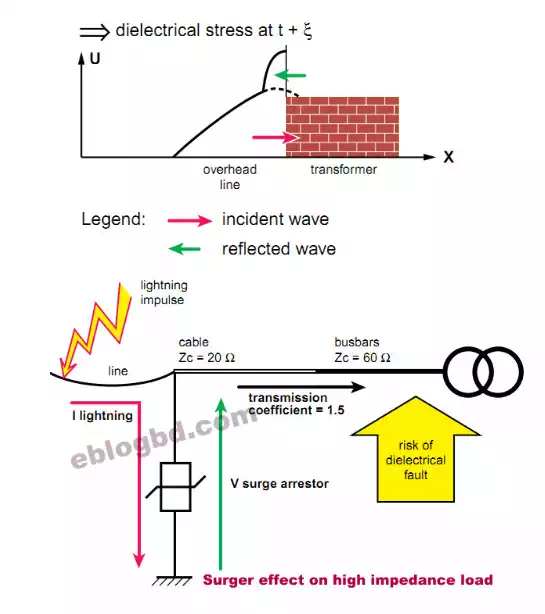
Surge effect on high impedance load
So Propagation of the voltage wave to a
conductor with a higher typical impedance, is conducted with a transmission
coefficient greater than 1. Due to this, the permissible dielectric stress may
be surpassed.
If there are no protection and flashover devices, calculations show that the voltage in the transformer’s inlet can progressively increase, by increments, up to the theoretical value which is twice the incident peak value (the increments are linked to the multiple reflections inside the substation).