Why electrical equipment’s rated in KVA not in KW
The ratings of all electrical equipments are all rated in KVA or Kilo Volt Amp. But the practical use is in KW. We can say it also that electrical equipments are rated in apparent power (KVA or VA) other then active power (KW or W).
Electrical equipments rated in KVA- the main reason
The ratings of all electrical equipments are all rated in KVA or Kilo Volt Amp. But the practical use is in KW. We can say it also that electrical equipments are rated in apparent power (KVA or VA) other then active power (KW or W).
The trend of electrical rating in terms of VA(volt amp), KVA(kilo volt amp), MVA(mega volt amp) is due to the variation in the consumer side. In consumer or user side the electrical parameters are so varieties that a manufacturer cannot cope of to all these variation. So the safe side is to rate the equipment in KVA.
The main criteria of the consumer side is variation in power factor– you cannot predict it. And KVA rating has no terms or influence of power factor as it is the direct multiplication of voltage and current. On the other hand the kw is calculated by power factor which a manufacturer cannot predict.
KW=V*I*(PF)
KVA=V*I
With KVA rating we can get the rated value of voltage and current. Say a small motor rated as 2KVA, we can get that its maximum current is 5amp with 400volt.
Say a high capacity power plant alternator is rated by 12MVA , 0.80 power factor. We can get the MW value with simple calculation (12*0.80=9.6) that is 9MW. So we can get it that the KVA rating is not fully sufficient, we need the power factor also if it is applicable.
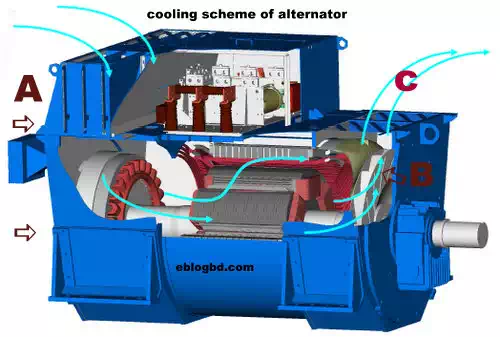
Cooling scheme of high capacity alternator
In alternator assembly there are rotor, excitation circuit and stator. As the design is compact and there are rotating part plus heavy current carrying involved- special cooling arrangement is needed. In generally simple force cooling method is utilized to cool high capacity alternator.
Generally the permissible temperature of rotor circuit is below 100. The temperature is observed in both the driving end(engine side) and non-driving end.
Forced air Cooling scheme in alternator.
The high capacity alternator
set is cooled by a shaft mounted fan and a forced cooling fan.
As seen from the figure A is front side where
there is rotor assembly with excitation circuit (non driving end)and B is back
side where the engine is mounted(driving end).
From front side there are 6 to 8 piece industrial grade net or sieve. These net restrict the dust or foreign material to enter and let air pass in. There is a high capacity external blower that force air towards these nets.
In B from figure, there is an internal fan blades assembly mounted on the shaft. It rotates by with the shaft. As it is driven by the engine- we can call it as mechanical blower.
In C there is exit path for hot air. The air exits vertically driven by the fan “B”.
So air enters in through “A”, driven by fan “B” then exits by path “C”.
Cooling scheme of high capacity alternator